-
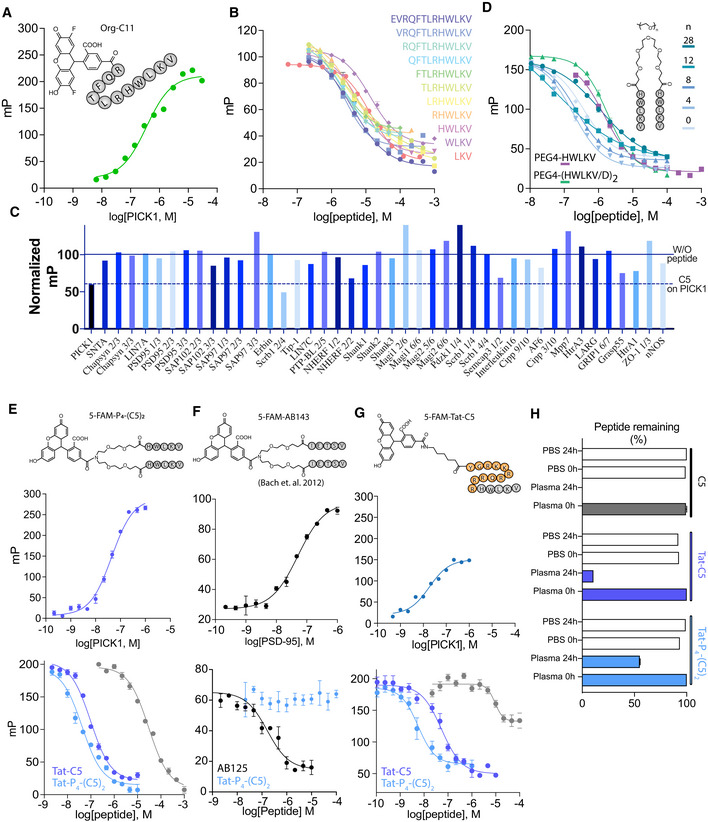
A
Fluorescence polarization saturation binding using Org‐C11 (20 nM) against an increasing concentration of PICK1.
-
B
Effects of truncation on competitive binding of DAT C‐terminal peptides to PICK1 using Org‐C11 (20 nM) as reporter.
-
C
Selectivity screen for Tat‐C5 against a selection of 42 purified PDZ domains, performed with a fixed concentration of C5 (10 μM) in competition with PDZ domains and their respective fluorescent ligands. Data are normalized to binding in absence of peptide (full line). Dashed line represents the level of competition obtained for PICK1.
-
D
Competitive binding curves of bivalent C5 PEGn variants. With PEG linker, length indicated.
-
E
Saturation (top) and competition binding curves using 5‐FAM‐PEG4‐(C5)2 (5 nM) and PICK1 against C5, Tat‐C5, and Tat‐P4‐(C5)2.
-
F
Saturation (top) and competition binding curves using 5‐FAM‐AB143 (5 nM) and PSD‐95 against AB125 (positive control), and Tat‐P4‐(C5)2.
-
G
Saturation (top) and competition binding curves using 5‐FAM‐Tat‐C5 (2 nM) and PICK1 against C5, TatC5, and Tat‐P4‐(C5)2.
-
H
Plasma stability as assessed by incubation of peptides as indicated with human plasma for 24 h followed by quantification by UPLC.
Data information: Data are shown as mean with error bars as SEM of
n ≥ 3. Binding curves were fitted to a log dose response (three parameters) extracting the K
d or IC
50 using GraphPad Prism 8.3.
K
i was calculated using the Cheng–Prusoff equation.