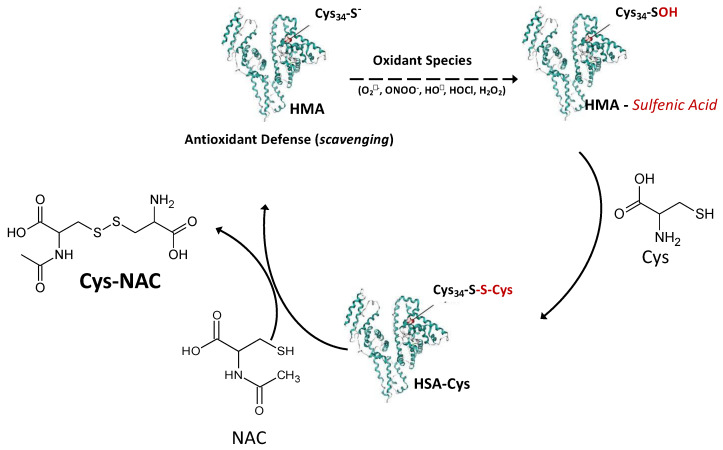
Figure 10.
Indirect antioxidant mechanism of NAC at extracellular level - Cys34 of mercaptoalbumin (HSA-SH) efficiently scavenges oxidant species forming the corresponding sulfenic acid which then reacts with Cys to form the cysteinylated adduct (HSA-Cys). NAC is able to selectively break the disulfide bond of HSA-Cys leading the disulfide NAC-Cys and the free form of Cys34 which in turn further acts as antioxidant.