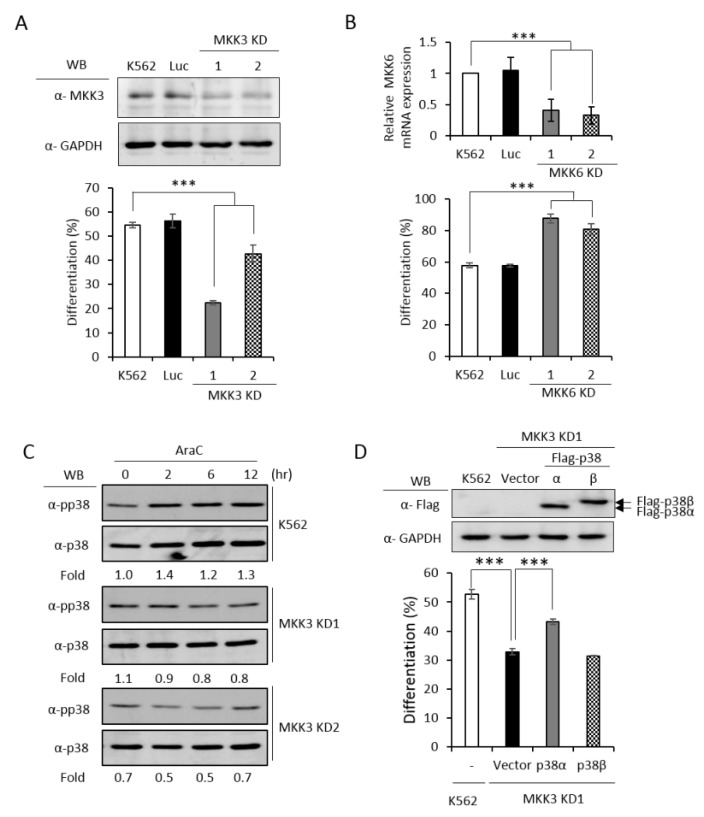
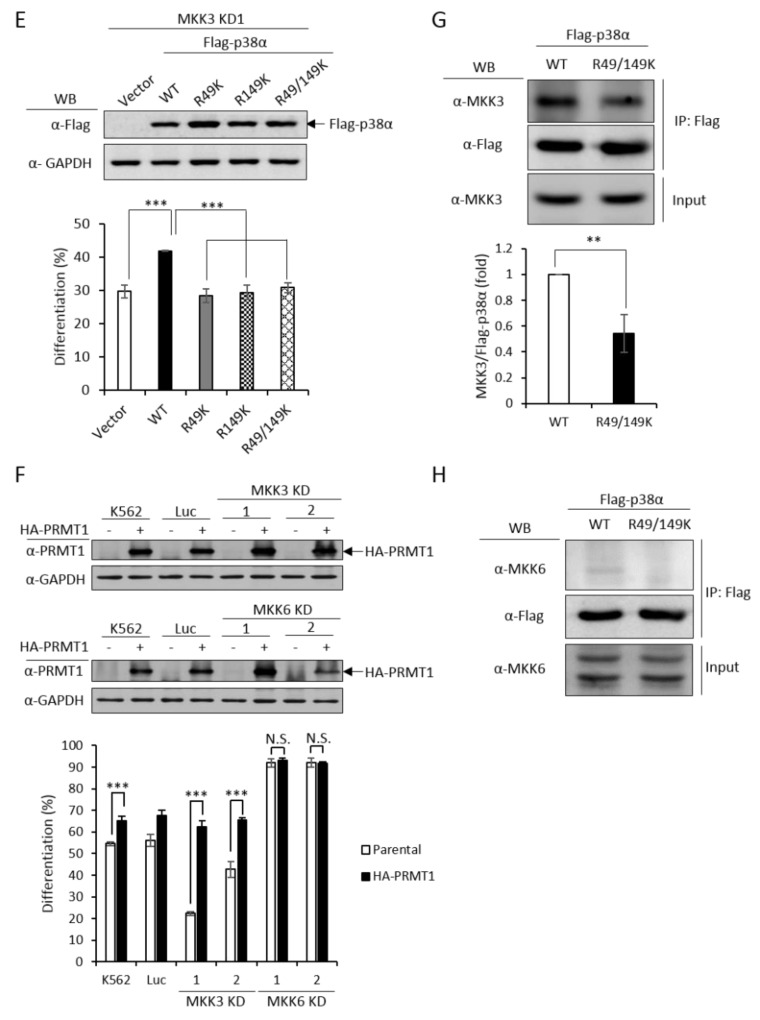
Figure 5.
PRMT1 acts downstream of M KK3 (MAPK kinase 3) to promote erythroid differentiation, and the R49/149K non-methylation mutant exhibits a reduced interaction with MKK3. MKK3 and MKK6 were knocked down (A) and (B) as described in the Methods section. AraC-induced erythroid differentiation was significantly suppressed in MKK3-knockdown (KD1 and KD2) cells (A); however it was stimulated in MKK6-knockdown (KD1 and KD2) cells (B). The activation of p38 was significantly reduced in MKK3 KD1 and KD2 cells (C). Ectopic expression of p38α, but not p38β, in MKK3 KD1 cells could partially rescue differentiation (D). However, the R49K, R149K and R49/149K mutants lost the ability to promote differentiation (E). Ectopic expression of HA-PRMT1 promoted differentiation in parental K562, Luc and MKK3 KD1 and KD2 cells but had no effect in MKK6 KD1 and KD2 cells (F). Luc is the vector control cell. To examine the interaction of p38α with MKK3 and MKK6, Flag-p38α wild type and R49/149K mutant proteins were expressed in p38α KD cells. After cells were stimulated with AraC (1 μM) for 5 h, Flag-p38α proteins were immunoprecipitated and the protein levels of MKK3 (G) or MKK6 (H) in the immunoprecipitates were examined by Western Blot. The levels of MKK3, pp38 and p38 were quantified by Multi-Gauge V3.0 analysis. All results shown are representatives of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed with results from three separate experiments. *** p < 0.005. ** p < 0.01.