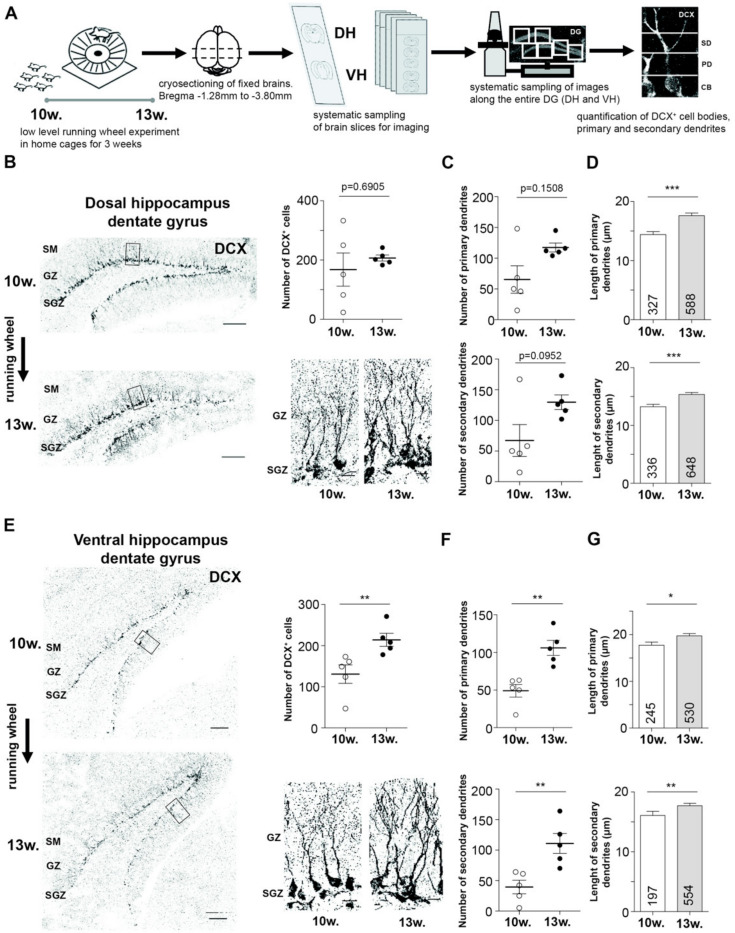
Figure 1.
Running wheel exposure differently impacts adult neurogenesis in the dorsal versus ventral hippocampus. (A) Scheme showing the experimental strategy to enhance neurogenesis by running wheel exposure and survey differences between dorsal and ventral dentate gyrus (DG). (B,E) Representative immunohistochemical stainings (left) including insets (right) against doublecortin (DCX) for immature neurons prior and upon running wheel exposure (left). Quantification of DCX+ cell numbers is shown (right) for dorsal (B) and ventral (E) DG. (C,F) Quantification of number of primary and secondary dendrites of DCX+ neurons in dorsal (c) and ventral (F) DG. (D,G) Quantification of the mean length of primary and secondary dendrites of DCX+ cells in dorsal (D) and ventral (G) DG. Number of circles represent different animals, n = 5 for each group, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, mean ± SEM, Scale bar overview: 100 µm, scale bar inset: 20 µm.