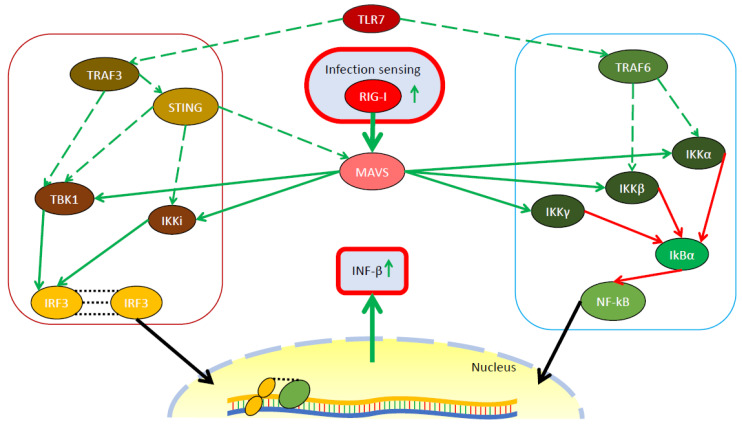
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the effect of SARS-CoV PLP on host cells’ immune system. The two proposed immune pathways affected by the SARS-CoV PLP are schematically represented here. Once the virus is detected by pathogen recognition receptors as RIG-I, the signal is transduced via MAVS to the activating kinases of the transcription factors: IRF3 and NF-kB. TBK1 and IKKi phosphorylate IRF3 and thus trigger its dimerization and nuclear translocation. IKKα-γ free NF-kB, that moves to the nucleus, by phosphorylating its inhibitor, IkBα. Activated STING and TRAF3 form complexes with IRF3 upstream regulators and thus increase the activation state. Finally, IRF3 and NF-kB promote the activation of the type I INF antiviral response. The PLP DUB activity antagonizes these pathways at multiple steps, resulting in a global antagonism of the signaling and lower activation of INF-β. For a detailed description of the interplays between the PLP and the proteins, the reader should refer to the text.