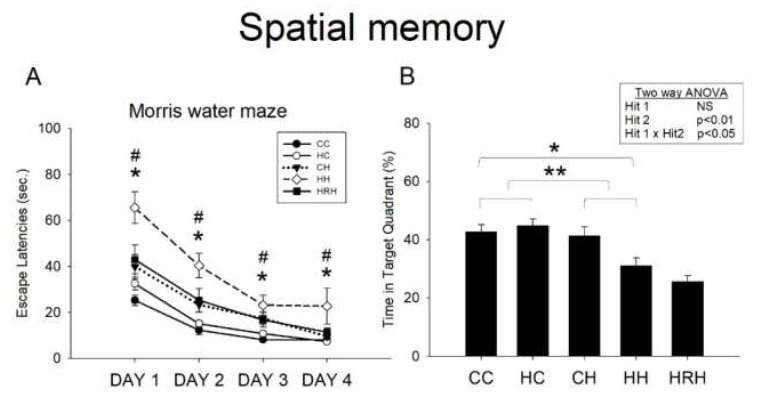
Figure 6.
Spatial learning and memory test assessed by the Morris water maze. (A) Escape latency to the platform in the Morris water maze (mean ± SEM). Rats in the HH group swam for a longer time to find the submerged platform on all four acquisition days compared to rats in the CC, HC, and CH groups. HRH group rats took less time to reach the platform compared to rats in the HH group. Maternal HFD/obesity on escape latencies: (F (1,36) = 13.949, p = 0.001). Postnatal HFD on escape latencies: (F (1,36) = 38.725, p < 0.001). An interaction between maternal obesity and postnatal HFD: (F (1,36) = 6.266, p < 0.05). (B) HH rats on average spent the least amount of time in the target quadrant on day five among the four experimental groups. However, there was no significant difference in the retention time between HH and HRH rats. A two-way ANOVA was used to assess the differences among groups in acquisition phase (repeated measure) and retention. The therapeutic effect of resveratrol was evaluated using the Student’s t-test. Postnatal HFD in target quadrant exploration: (F (1,36) = 8.094, p < 0.01). An interaction between maternal high-fat/maternal obesity and postnatal HFD in target quadrant exploration: (F (1,36) = 5.147, p < 0.05). * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05 vs. CC; # p < 0.05 vs. HRH.