Figure 1.
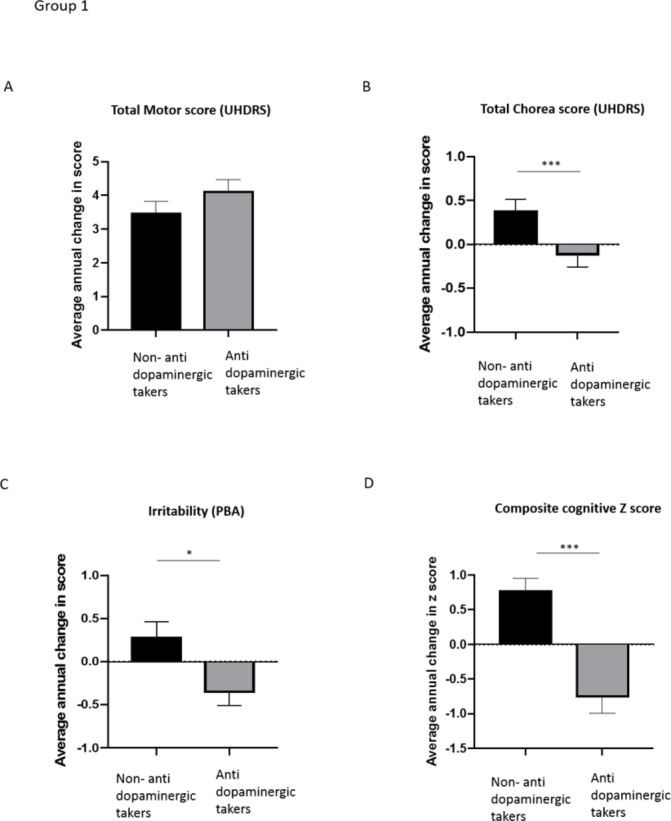
Graphs showing average annual change in UHDRS total motor score, PBA irritability and composite cognitive score per group. Group 1. (A) There is no difference in the annual increase in UHDRS total motor score between HD antidopaminergic medication takers and HD non-antidopaminergic medication takers. (B) HD patients taking antidopaminergic medication had a significantly reduced increase in chorea score compared with HD controls not taking antidopaminergic medication. (C) Antidopaminergic medication takers had a significantly smaller increase in reported irritability on the PBA compared with patients not on DA altering medications.(D) HD antidopaminergic medication takers had a statistically faster rate of cognitive decline than HD patients not taking these drugs. Groups were compared using univariate analysis with age, CAG and gender as covariates. Mean and SE of the mean are shown. ***p<0.001. n=466 per group. DA, dopamine; HD, Huntington’s disease; PBA, problems behavioural assessment; UHDRS, Unified Huntington Disease Rating Scale.
