Figure 1.
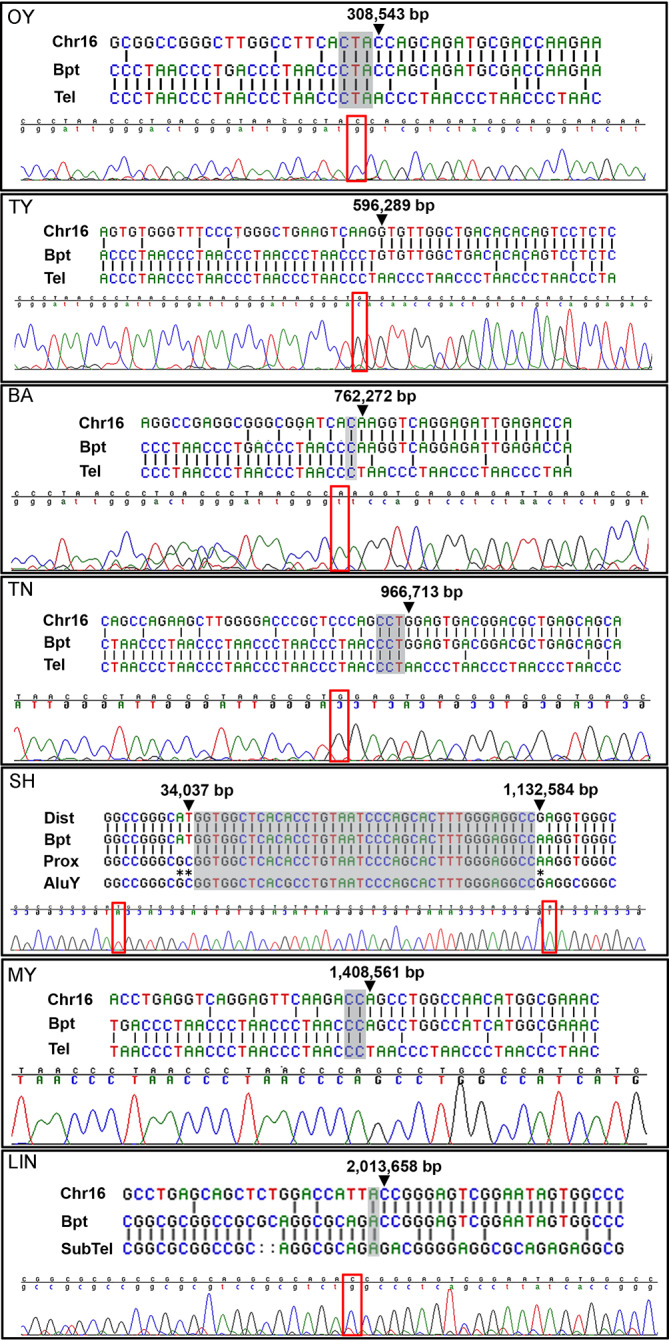
Chromosome 16 breakpoint sequences. DNA sequences at ATR-16 breakpoints. Patient codes are given in the upper left of each panel. For each case, alignment of the two normal sequences is shown with sequence from the derivative chromosome (upper) with chromatogram traces traversing each breakpoint (lower). Areas of ambiguity are highlighted with grey boxes and the location of the last unambiguous base pair(s) are denoted by arrowheads and red boxes. Chr16, normal chromosome 16 sequence; Bpt, breakpoint sequence; Tel, telomere repeat sequence; SubTel, subtelomere repeat sequence; Prox, proximal chromosome 16 sequence; Dist, distal chromosome 16 sequence; AluY, AluY repetitive element. Asterisks indicate informative polymorphisms allowing sequence origins to be identified. For patients MY and OY, a telomere primer with a mismatched G nucleotide was used.
