Figure 1.
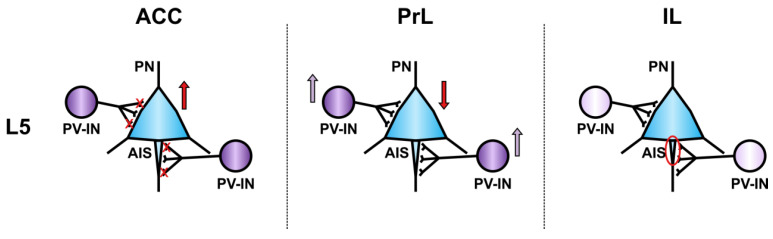
Subregion-specific modification of mPFC L5 pyramidal neurons by PV+ GABAergic interneurons in pathological pain. In the ACC, the number of synapses formed by PV+ interneurons (PV-IN, purple) is decreased (red crosses), which leads to disinhibition of pyramidal neurons (PN, blue) and hyperexcitability; in the PrL, PV+ interneurons increase their feed-forward inhibition onto pyramidal neurons, thereby decreasing pyramidal neuron excitability; in the IL, PV content is decreased (faint purple) in PV+ interneurons and axon initial segment (AIS) of pyramidal neurons is shortened (red circle), which has been associated with decreased pyramidal neuron excitability [90].