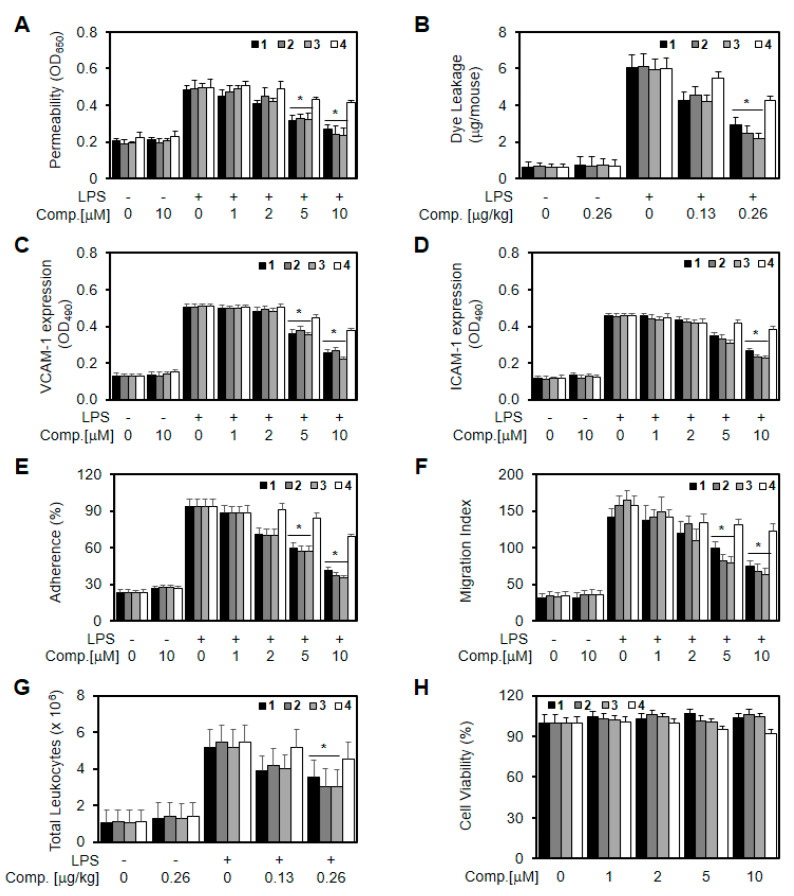
Figure 3.
Effects of compounds (1–4) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated vascular inflammatory responses. (A) Effect of various concentrations of compounds (1–4) on LPS-induced (100 ng/mL, 4 h) barrier disruption was monitored by the flux of Evans blue bound albumin across human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs); (B) Effect of compounds (1–4) on LPS (15 mg/kg, i.p.)-induced vascular permeability in mice was examined by the flux of Evans blue in mice (expressed μg/mouse, n = 5); LPS-mediated (100 ng/mL) expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) (C) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) (D) in HUVECs was analyzed after treating monolayers with each compound (10 μM each) by whole cell enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); (E) LPS-mediated (100 ng/mL) adherence of monocytes to HUVEC monolayers was analyzed after treating cells with each compound; (F) LPS-mediated (100 ng/mL) migration of human neutrophils through HUVEC monolayers was analyzed after treating cells with each compound; (G) The effects of each compound on LPS (15 mg/kg, i.p.)-induced leukocyte migration in mice (expressed ×106, n = 5); (H) The effects of each compound on cell viability were evaluated using CCK8 assays. The results are expressed as the means ± SEM of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05 vs. LPS.