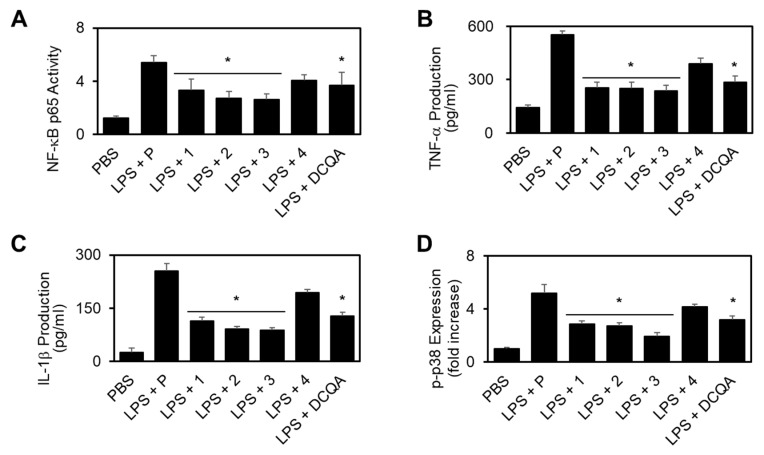
Figure 4.
Effect of new compounds (1–4) on the LPS-stimulated activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), the production of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)/ interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and the phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). First, 20 μM of 3-5-di-O-dihydrocaffeoylquinic acid (DCQA) was used as positive control. (A) LPS (100 ng/mL)-mediated activation of NF-κB p65 in HUVECs was analyzed after the treatment of cells with 10 μM of each compound for 6 h; LPS (100 ng/mL)-mediated production of TNF-α (B) or IL-6 (C) in HUVECs was analyzed after the treatment of cells with the indicated concentrations of each compound for 6 h; (D) HUVECs were activated with LPS (100 ng/mL), followed by treatment with each compound at different concentrations for 6 h. The effects of each compound on the LPS-mediated expression of phospho-p38 were determined by ELISA. * p < 0.05 vs. LPS.