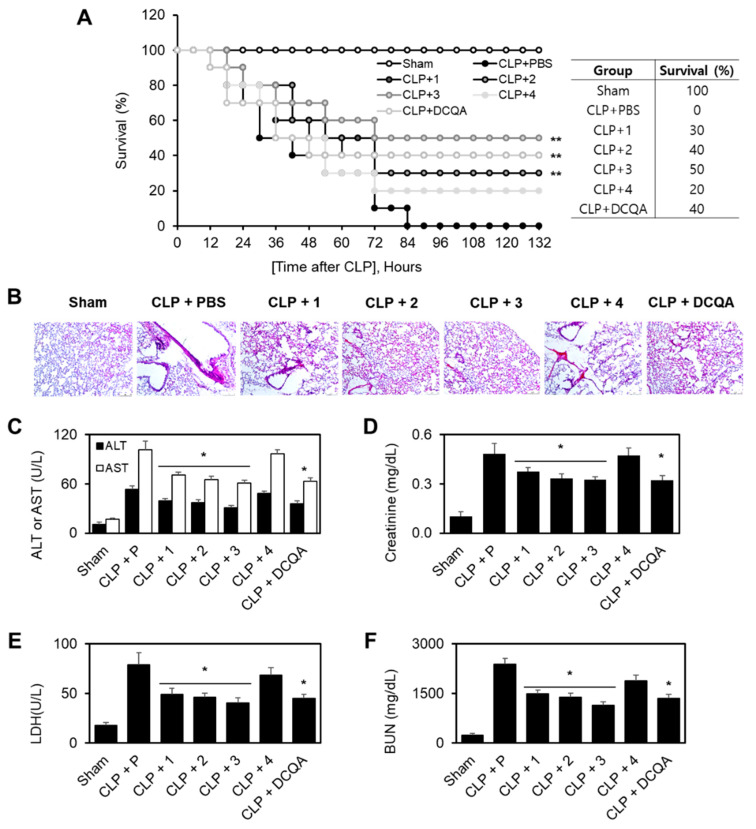
Figure 5.
Effects of each compound on cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced mortality and pulmonary injury. (A) Male C57BL/6 mice (n = 10) were intravenously treated with each compound (0.26 mg/kg) or DCQA (1 mg/kg, positive control at 12 and 50 h after CLP. Animal survival was monitored every 6 h after CLP for 132 h. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis was performed for evaluating of the overall survival rates; (B) Male C57BL/6 mice underwent CLP and were administered each compound (0.26 mg/kg) intravenously at 12 and 50 h after CLP (n = 5). Mice were killed 96 h after CLP. Photomicrographs of lung tissues (H&E staining, 200×, White scale bar = 50 µm). The illustrations show representative images from three independent experiments; (C–F) The same as (B,C) except that mice were bled to death. Aspartate transaminase (AST) (C), alanine transaminase (ALT) (C), creatinine (D), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) (E), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (F) levels in the plasma were measured. The results are expressed as the means ± SD of five independent experiments (n = 5). * p < 0.05 vs. the CLP group.