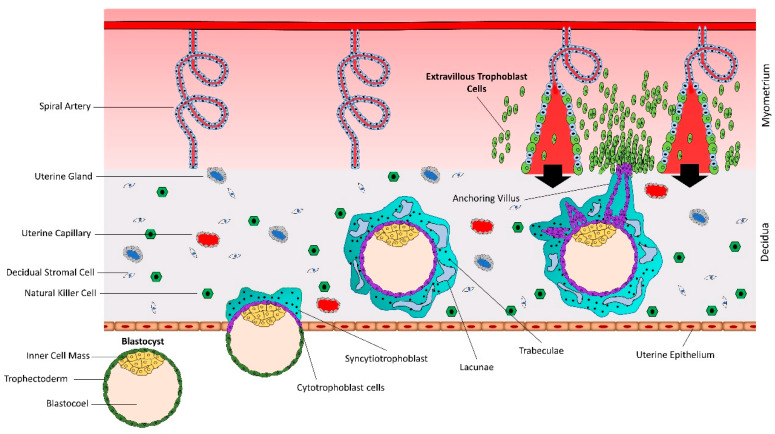
Figure 1.
Early placental development and spiral artery remodeling. Human placental development starts with interaction between hatched blastocyst and uterine epithelium. The trophoblast cells that contact with the uterine epithelium transform into highly proliferative cytotrophoblasts (CTBs). Cytotrophoblasts undergo rapid proliferation and some of them fuse to form a multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast (STB). Within a few hours, STB expands and covers whole blastocyst and helps in blastocyst invasion into the uterine decidua. Continuous proliferation of CTBs results in formation of villi. Some CTBs from the tip of anchoring villi break the STB cover, invade the uterine stroma and myometrium, and transform into extravillous trophoblast cells (EVTs). EVTs remodel the spiral arteries to ensure sufficient flow of blood to the placenta.