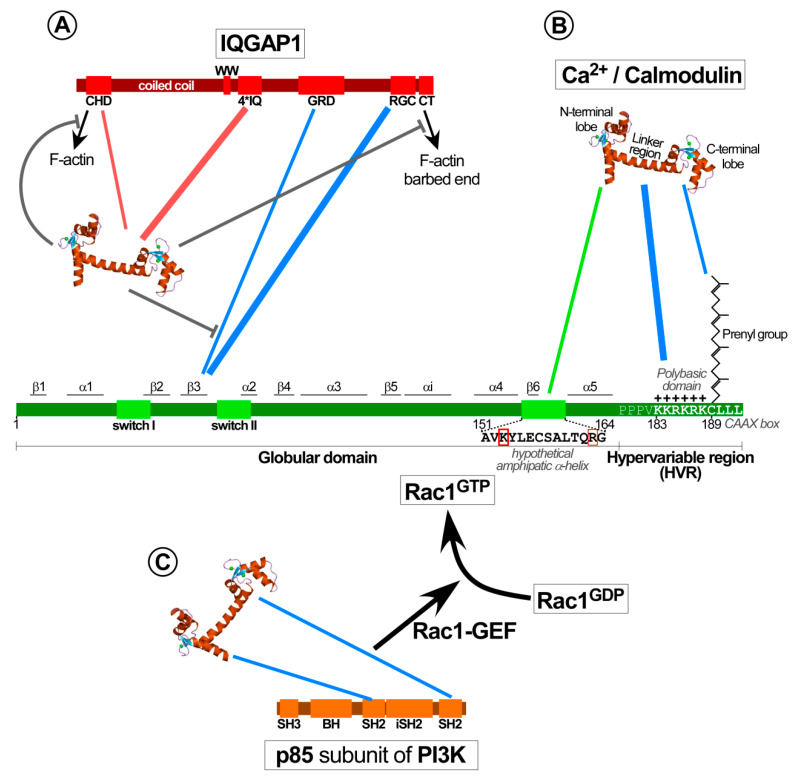
Figure 4.
Calmodulin regulates Rac1 signalling through direct and indirect protein–protein interactions. The scheme summarizes the multiple interactions between calmodulin, Rac1, isoleucine–glutamine (IQ) Motif Containing GTPase Activating Protein 1 (IQGAP1) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). Ca2+/calmodulin affects Rac1 signalling outcome by directly interacting with Rac1 (A), modulating IQGAP1/Rac1 interaction (B) or activating PI3K (C). (A) Multiple Rac1 domains directly interact with Ca2+/calmodulin. Similar to the KRas/calmodulin interaction (see Section 3.3 and Figure 1), the polybasic domain (PBR) and the geranylgeranyl group (prenyl) within the hypervariable region (HVR) of Rac1 are both essential for Ca2+/calmodulin binding (blue lines). Based on the well-characterized KRas/calmodulin interaction, one can speculate that the linker domain and C-terminal lobe of calmodulin interact with the PBR and prenyl group of Rac1, respectively. In addition, amino acids 151-164 in Rac1 may adopt an amphipathic α-helix that contributes to calmodulin interaction (green line) and Rac1 activation. Within this region, the basic amino acid K153 (thick red square), and to a lesser extend R163 (red square) are critical for the interaction with the N-terminal lobe of calmodulin. The position of the switch I and II domains, the PBR (aa 183-188) and the prenyl group attached to C189 of Rac1 are indicated. The N- and the C-terminal lobes and the linker region of calmodulin as well as two bound Ca2+ ions in each lobe are also shown. (B) IQGAP1 interaction with active Rac1 (Rac1-GTP) is inhibited by Ca2+/calmodulin. The Ras GAP-related domain (GRD), RASGAP C-terminal (RGCT) and C-terminal (CT) regions of IQGAP1 bind to the switch I and switch II domains of Rac1-GTP (blue lines) to maintain Rac1 in its active state. Ca2+/calmodulin binds to the four isoleucine/glutamine-containing (IQ) motifs (thick red line) within IQGAP1, which abrogates IQGAP1/Rac1 interaction. In addition, Ca2+/calmodulin binds to the N-terminal calponin homology domain (CHD) (red line) of IQGAP1. This impairs IQGAP1 interaction with F-actin, blocking IQGAP1 from stimulating F-actin crosslinking, bundling, and capping. The CHD, coiled-coil repeat (CC), tryptophan-containing proline-rich motif (WW), IQ, GRD, RGCT and CT domains of IQGAP1 are indicated (see Section 4.2.2 for details) (C) Ca2+/calmodulin interacts and activates PI3K. The N- and C-terminal lobes and the flexible central linker of Ca2+/calmodulin bind to the N-terminal (nSH2) and C-terminal (cSH2) domains of the p85 subunit of PI3K (blue lines). This interaction releases the p85-mediated autoinhibition of the catalytic p110 subunit of PI3K. Activated PI3K then phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate (PI(4,5)P2) and generates phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PI(3,4,5)P3), which can bind and activate several Rac1 guanine nucleotide exchange factors (Rac1 GEFs) to increase Rac1-GTP levels (see Section 4.3 for further details).