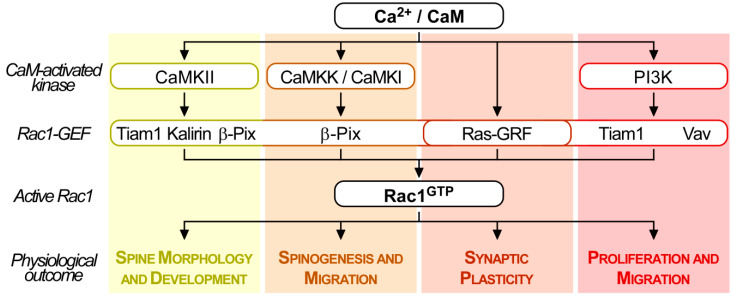
Figure 5.
Calmodulin-mediated activation of Rac1-specific GEFs controls multiple Rac1-dependent cellular functions. This scheme highlights the ability of Ca2+/calmodulin (Ca2+/CaM) to bind and activate several kinases, including calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I and II (CaMKI, CaMKII), CaMK kinase (CaMKK) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). This leads to the activation of Rac1-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factors (Rac1-GEFs), including T-lymphoma invasion and metastasis-inducing protein 1 (Tiam1), PAK-interacting exchange factor β (β-PIX), kalirin, Ras guanine nucleotide releasing factor (RasGRF), and Vav. These Rac1-GEFs then promote GTP loading of Rac1, promoting Rac1 activation, which is associated with fundamental cellular activities, including spine morphology and development, spinogenesis, synaptic plasticity, proliferation, and migration (see text for further details).