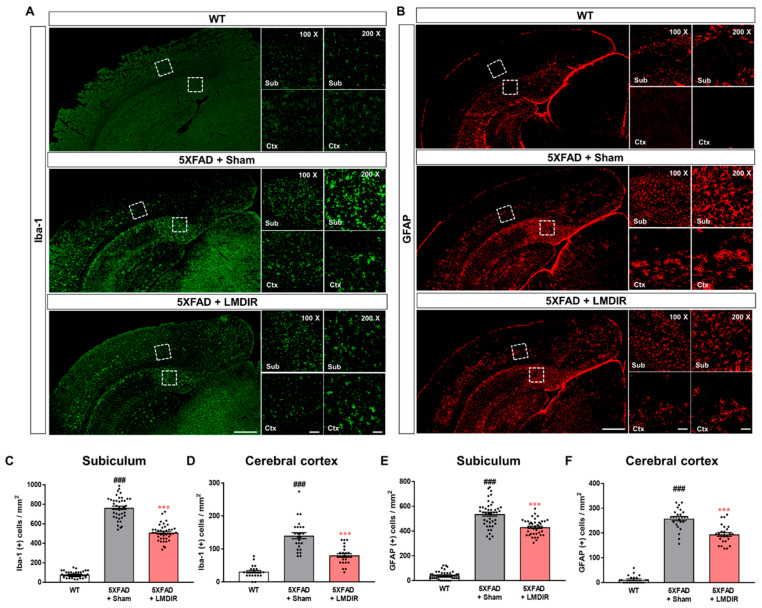
Figure 3.
Inhibitory effect of LMDIR on neuroinflammation in the subiculum and cerebral cortex of 5XFAD mice. (A) Representative images of immunofluorescent staining of the subiculum and cerebral cortex for Iba-1, a marker of microglia. (B) Representative images of immunofluorescent staining of the subiculum and cerebral cortex for GFAP, a marker of astrocytes. (C,D) The number of Iba-1 (+) cells was significantly higher in the subiculum and cerebral cortex of 5XFAD mice than that of the WT mice. In contrast, the number of Iba-1 (+) cells was significantly lower in the subiculum and cerebral cortex of LMDIR-exposed 5XFAD mice than that of the sham-exposed 5XFAD mice. (E,F) The number of GFAP (+) cells was significantly higher in the subiculum and cerebral cortex of 5XFAD mice than the WT mice. However, the number of GFAP (+) cells was significantly lower in the subiculum and cerebral cortex of LMDIR-exposed 5XFAD mice than that of the sham-exposed 5XFAD mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 7 in each group). ### p < 0.001: WT mice versus sham-exposed 5XFAD mice. *** p < 0.001: sham-exposed 5XFAD mice versus LMDIR-exposed 5XFAD mice. Scale bar = 50 and 100 μm (Sub and Ctx) or 500 μm (hemisphere). LMDIR, low–moderate dose ionizing radiation; Iba-1, ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein.