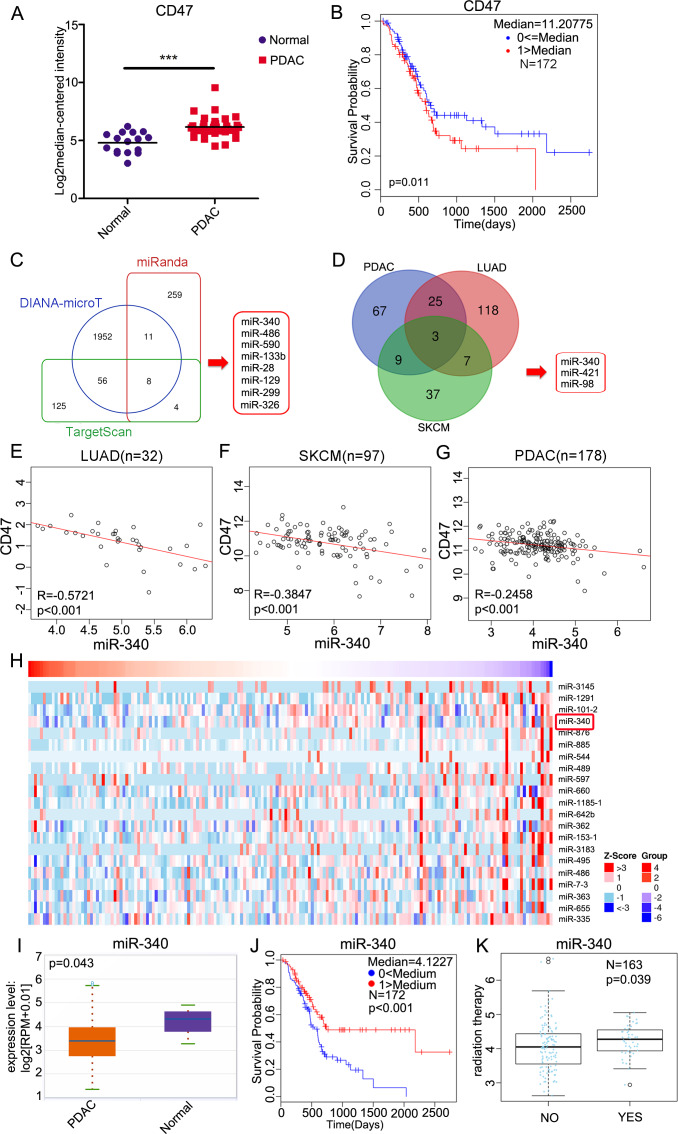
Figure 1.
miR-340 is negatively correlated with the expression of CD47 and overall survival in PDAC. (A) Analyses of CD47 expression in normal pancreas (n=16) and pancreatic carcinoma tissues (n=36) by the Oncomine database (p<0.001). (B) The Cox regression analysis revealed a correlation between higher CD47 expression and a poorer prognosis in 172 patients with PDAC analyzed using the LinkedOmics database (p=0.011). (C) Bioinformatics predictions of miRNAs targeting CD47 by miRanda, DIANA-microT and TargetScan. (D) LinkedOmics-identified miRNAs that were significantly negatively correlated with CD47 in PDAC, LUAD and SKCM. (E) The correlative analysis of miR-340 and CD47 in human LUAD (n=32), (F) SKCM (n=97) and (G) PDAC (n=178). (H) Heat map of miRNAs that were negatively correlated with CD47 in PDAC. (I) Analyses of miR-340 expression in normal pancreas (n=4) and pancreatic carcinoma tissues (n=178) by starBase (p=0.043). (J) Cox regression analysis performed using the LinkedOmics database revealed a correlation between miR-340 and survival probability in 172 patients suffering from PDAC (p<0.001). (K) Graphs show the impact of radiation therapy on the expression of miR-340 in PDAC (p=0.039). The data in A and I were analyzed by two-tailed, unpaired t-test. The data in B and J were analyzed by the log-rank Mantel–Cox test. Spearman correlation analysis was used in E–G. The data in K were analyzed using a two-sided Wilcox test. LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma; PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; SKCM, skin cutaneous melanoma.