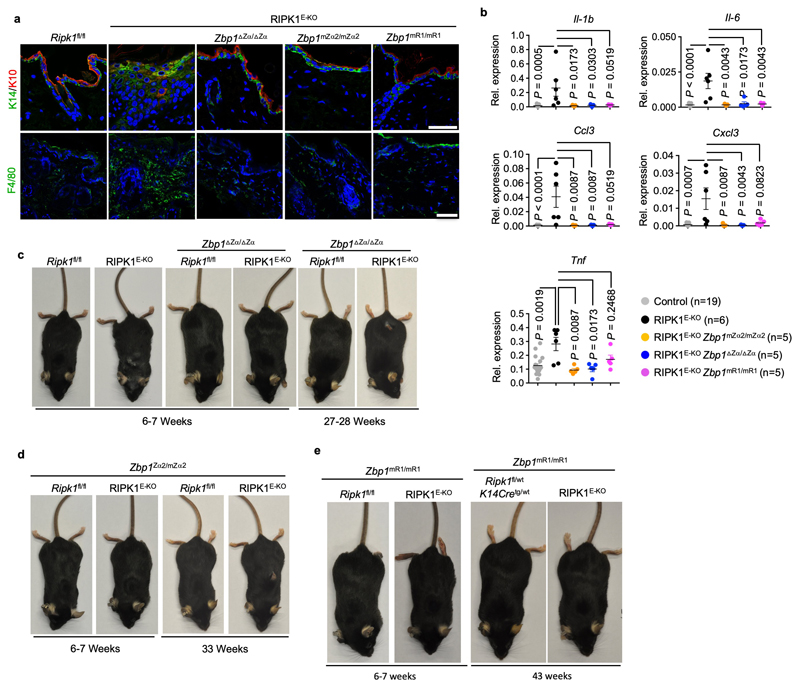
Extended Data Figure 3. ZBP1 causes keratinocyte necroptosis and skin inflammation in RIPK1E-KO mice by Zα-dependent and -independent mechanisms.
a, Representative images of skin sections from 6 - 7 week-old mice with the indicated genotypes immunostained with the indicated antibodies and DAPI (DNA stain). RIPK1E-KO (n ≥ 5); RIPK1E-KO Zbp1mZα2/mZα2 (n ≥ 3); RIPK1E-KO Zbp1∆Zα/∆Zα (n ≥ 3); RIPK1E-KO Zbp1mR1/mR1 (n ≥ 3). Scale bars, 50 μm. b, qRT-PCR analysis of the mRNA expression of the indicated cytokines and chemokines in RNA isolated from total skin from 6 - 7 week-old mice with the indicated genotypes. Each dot represents an individual mouse. Data show mean ± s.e.m. P value by two-sided nonparametric Mann–Whitney test. Control mice include Ripk1FL/FL mice that do not express K14-Cre, or Ripk1FL/WT K14-Cre mice, with WT or mutated Zbp1 alleles. c-e, Representative images of mice with the indicated genotypes at the indicated age. RIPK1E-KO (n = 6) and RIPK1E-KO Zbp1∆Zα/∆Zα (n = 17) (c); RIPK1E-KO Zbp1mZα2/mZα2 (n = 16) (d); RIPK1E-KO Zbp1mR1/mR1(n = 20) (e).