FIGURE 5.
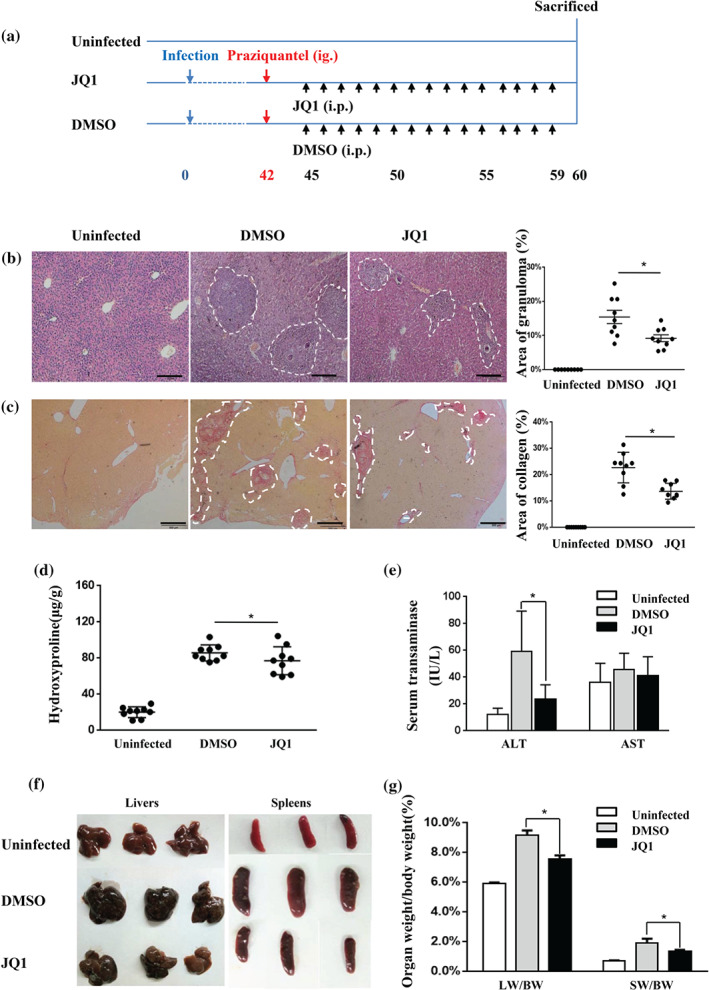
JQ1 treatment ameliorates hepatic immunopathology in S. japonicum‐infected mice. (a) Experimental design of JQ1 study on animals. Mice were infected percutaneously with S. japonicum cercaria at Day 0. Praziquantel (300 mg·kg−1) was administered once by gavage at 42 days. Daily i.p. injections of JQ1 or DMSO were conducted from Days 45 to 59. Animals were then killed for tissue collection at 60 dpi along with age‐ and sex‐matched control mice. Liver sections (4 μm) from infected and control mice were stained with either HE or Sirius Red. (b) Representative HE staining and (c) representative Sirius Red staining of liver sections of the indicated groups (three mice per group) are shown. Percentages of granulomatous and fibrosis areas were quantified and are shown on the right side in (b) and (c) respectively. Magnification was 40×. Bar = 200 μm. (d) Hydroxyproline was quantified in the livers of infected and control mice. (e) Serum ALT/AST levels are shown as the mean ± SEM. (f) Representative photograph of livers and spleens from S. japonicum‐infected mice treated with JQ1 or DMSO (three mice per group) are shown. (g) The liver and spleen weight to body weight ratio (LW/BW and SW/BW respectively) were calculated. All data were expressed as mean ± SEM pooled from three independent experiments (with three mice per group per time), n = 9 mice per group, * P < .05, compared to DMSO treatment (one‐way ANOVA)
