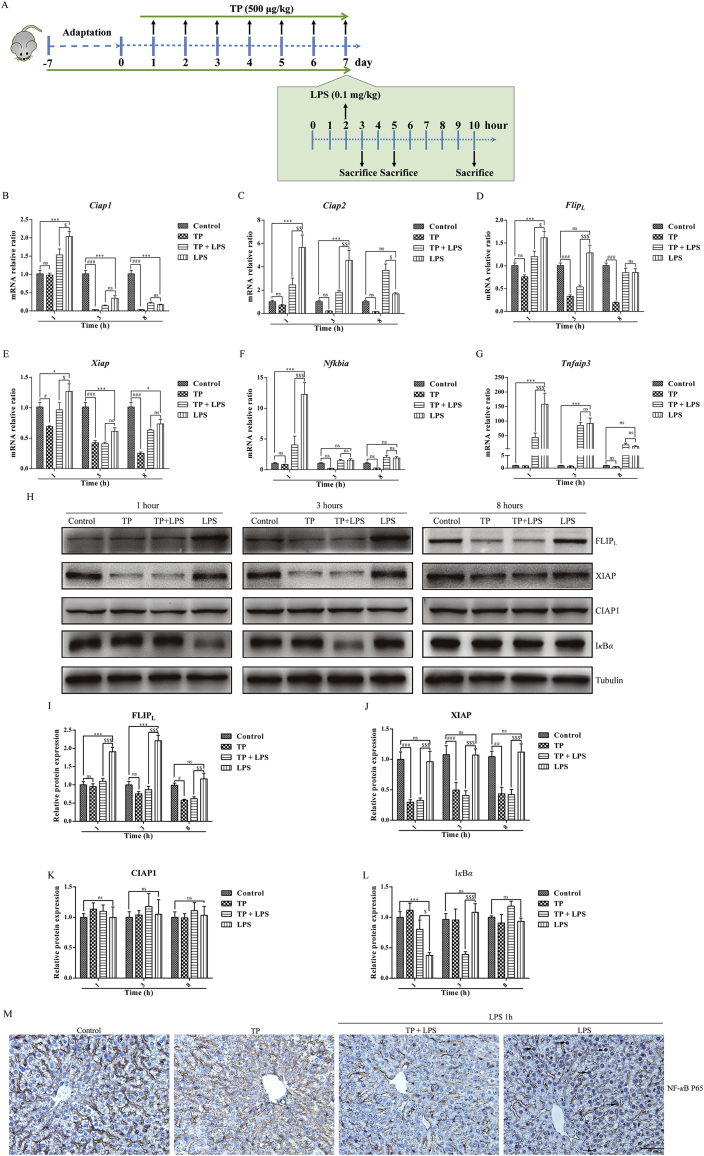
Figure 4.
Possible role of NF-κB and NF-κB-mediated pro-survival signals in TP/LPS-induced hepatotoxicity. (A) Experimental design to detect the time-dependent changes of NF-κB and its related pro-survival factors. (B)–(G) Relative mRNA levels of NF-κB target genes, including Ciap1, Ciap2, FlipL, Xiap, Tnfaip3, and Nfkbia, were detected by qPCR with tubulin as the internal control (n = 6). (H)–(L) Representative Western blots and relative intensity of protein bands of FLIPL, CIAP1, XIAP, and IκB-α after the treatment of TP and LPS with tubulin as the loading control (n = 4–6). (M) Representative photomicrographs of liver sections by IHC for P65 1 h after LPS application (200 × ). Scale bar = 50 μm. Results were expressed as mean ± SEM and statistical analysis was performed using Two-way ANOVA following by Tukey's multiple comparison test. *, #, $P<0.05, **, ##, $$P<0.01, ***, ###, $$$P<0.001; ns, no statistical difference.