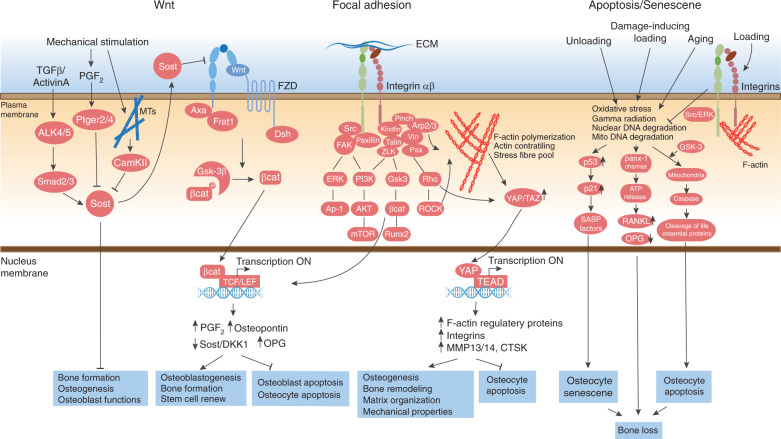
Fig. 8.
Signaling pathways involved in osteocyte mechanobiology. The Wnt/β-Catenin pathway mechanistically, the canonical Wnt/β-Catenin pathway is activated through the binding of Wnt ligands to a coreceptor complex consisting of Lrp5 or Lrp6 and FZD.152,153 This binding further activates the intercellular effector Dsh by FZD-mediated phosphorylation. Activated Dsh leads to the phosphorylation of Gsk-3β, which inhibits free β-Catenin in the cytosol by phosphorylating β-Catenin at multiple serine/threonine sites. Once Gsk-3β is phosphorylated by Dsh, it releases captured β-Catenin. As a result, free β-Catenin is translocated to nuclei, where it binds the coeffectors Tcf and Lef, inducing downstream gene transcription. Downstream effects of β-Catenin include the expression of Wnt target genes154 and secretory proteins (Opg, Osteopontin)157,161 and load-induced PGE2 secretion.164 Sclerostin antagonizes Wnt signaling through its competitive binding to Lrp5 and Lrp6 at their first two YWTD-EGF repeat domains.181 Mechanical stimulation can suppress Sost expression through both Peger2/4 and the MT pathway. In addition, the Tgfβ-Smad2/3 pathway can enhance sclerostin expression. As a result, during the osteocyte mechanotransduction process, the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway enhances osteoblastogenesis and bone formation; however, sclerostin negatively regulates the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway. Focal adhesion As the central proteins in the FA complex, Integrins, especially Integrin β subunits, are essential for bone development and osteocyte mechanotransduction. The “Integrin adhesome” is a network of 156 proteins in the FA complex.166 In the FA complex, Kindlin-2, Talin, and other structural proteins are directly linked to the cytoplasmic tail of the Integrin β subunit, which further connects with the Pinch, Paxillin, Vinculin, and Arp2/3 proteins.23,79 This Integrin adhesome complex links the ECM and F-actin cytoskeleton and enhances the activation of downstream pathways, such as the Erk, PI3K, Gsk3, and Rho pathways. Upon F-actin cytoskeleton polymerization, YAP/TAZ coordinate signals from Rho GTPase and tension of the actomyosin cytoskeleton, initiate downstream target gene expression, and finally enhance osteogenesis and bone remodeling and inhibit osteocyte apoptosis. Apoptosis/senescence osteocyte apoptosis, a form of programmed cell death, and senescence, a death-resistant cell fate program, are common features of aging bone tissue. Appropriate mechanical stimulation prevents osteocyte apoptosis, whereas aging, damage-inducing loading and disuse induce osteocyte apoptosis174 and senescence177 through several different pathways. In contrast, mechanical stimulation induces Src/Erk activation through Integrin and the cytoskeleton in osteocytes, inhibits apoptotic and senescence-related pathways and supports osteocyte survival.172