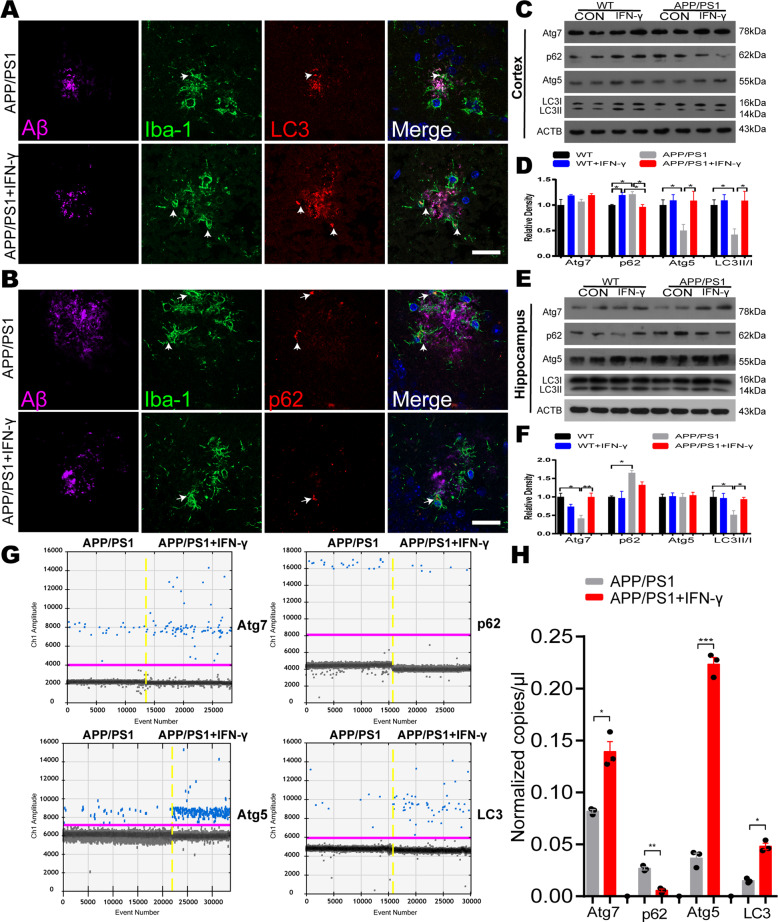
Fig. 1. IFN-γ administration induces autophagy in APP/PS1 mice.
a, b Triple immunostaining of mouse brain slices with anti-Aβ (purple), anti-Iba-1 (green) and anti-LC3/anti-p62 (red) antibodies to examine autophagy in APP/PS1 mice treated with IFN-γ or not. Hoechst (blue) was used for nuclear staining. Scale bar = 10 μm. c, d Western blots of cortical proteins probed with the indicated antibodies. Atg7 expression was not significantly different among the four groups. The p62, Atg5 and LC3II/I levels were different among the four groups. e, f Western blots of hippocampal tissues probed with the indicated antibodies. Atg5 expression was not significantly different among the four groups. Atg7 and LC3II/I levels were different among the four groups. g, h Droplet digital-PCR analysis of autophagic genes in the APP/PS1 mice treated with IFN-γ or not. g Representative ddPCR reads of cDNA samples from the microglia labeled with TMEM119 antibodies in APP/PS1 mice. h ddPCR reads of autophagic genes (Atg7, p62, Atg5 and LC3) copies from the microglia in APP/PS1 mice were represented as bar graph. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. The results are all shown as the mean ± SEM. (n = 3/group).