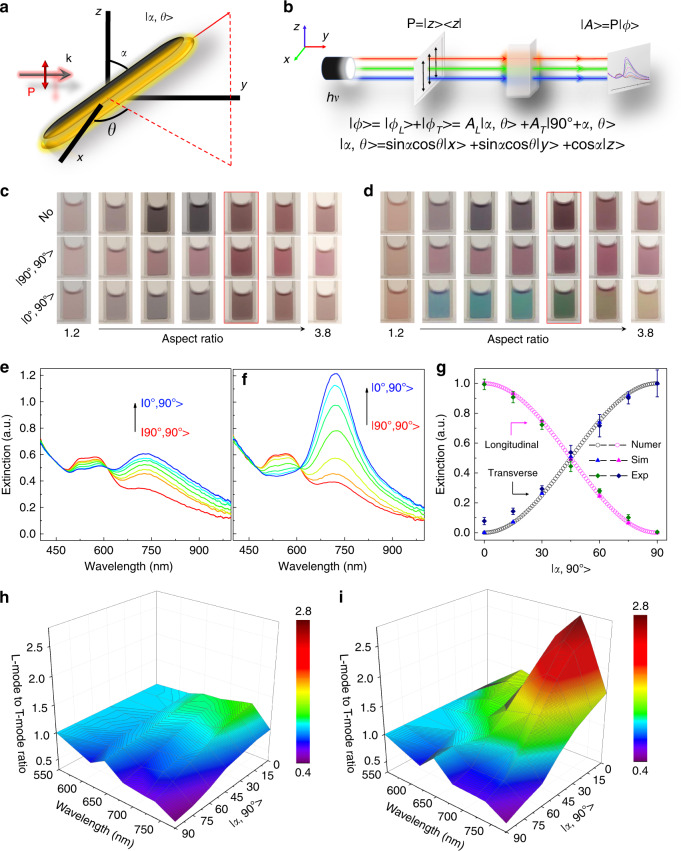
Fig. 2. Optical tunability of colloidal cAuNRs.
a Schematic illustration of cAuNRs under the orientational state |α, Ɵ > with respect to the polarization of light. b Tuning plasmonic extinction of cAuNRs under polarized light and the corresponding mathematical interpretation by bra-ket notation. c, d Digital images of cAuNRs dispersions under normal (c) and polarized light (d). In both c and d, the colloidal dispersions from left to right correspond to spectra in Supplementary Fig. 2f (from bottom to top). e, f Tuning the extinction of cAuNRs under normal (e) and polarized light (f) for samples of highlighted columns in (c) and (d), respectively. e, f share the same y axis. The spectra were measured with an angle step of 15o. g Correlation between the excitation modes and orientational states of cAuNRs, with the fine spectra tunability shown in f. The abbreviations, Numer, Sim, and Exp, represent numerical, simulation, and experimental results, respectively. Error bars represent the standard deviations from three experimental measurements. h, i Summary of L-mode to T-mode ratio of different dispersions in c and d achieved by varying α under normal (h) and polarized light (i). The azimuth angle, Ɵ, was set at 90o. P and k are the polarization and wave vector of the incident light, respectively.