Fig. 1.
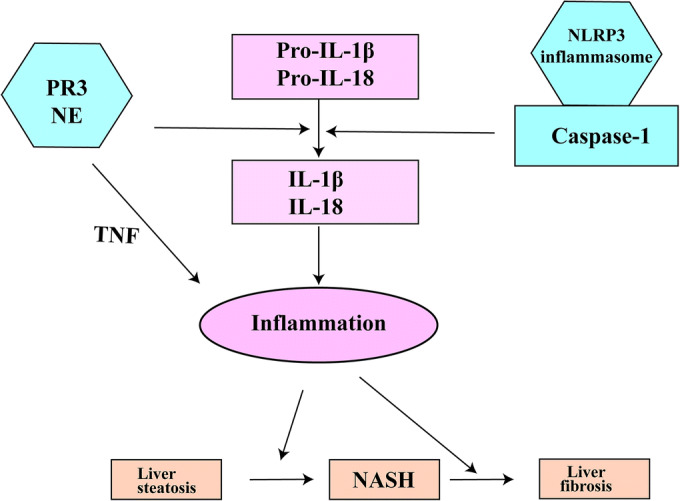
The role of IL-1β activation pathways in NAFLD. Pro-inflammatory cytokines contribute to NAFLD development from liver steatosis to NASH and fibrosis by activating sterile inflammation in the liver. Some of these cytokines such as IL-1β and IL-18 are secreted as inactive and need proteolytic cleavage in order to become active. Two mechanisms responsible for IL-1 cytokine activation are represented by the NLRP3 inflammasome-caspase-1 protein complex and the neutrophil serine proteases PR3 and NE. Additionally to IL-1β and IL-18, PR3 and NE are able to activate membrane-bound TNF. Activating pro-inflammatory NLRP3 inflammasome-caspase-1 complex and the neutrophil serine proteases also contributes to NAFLD development and progression. IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-18, interleukin-18; NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; NE, neutrophil elastase; PR3, proteinase-3; Pro-IL-1β, pro-interleukin-1β; Pro-IL-18, pro-interleukin-18; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
