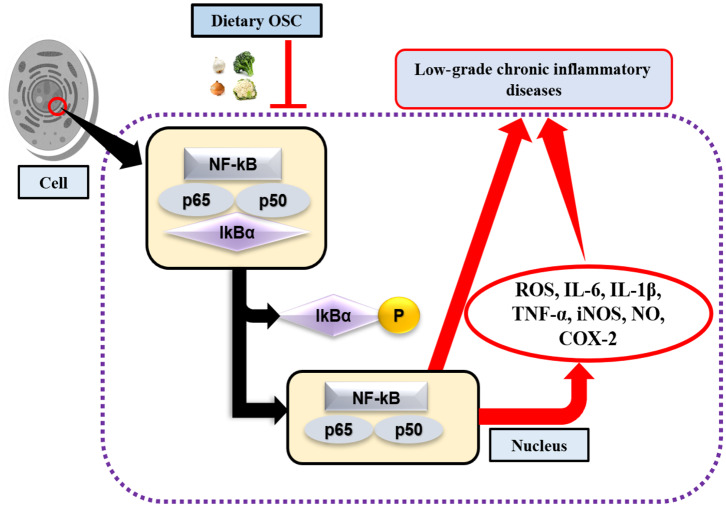
Figure 2.
OSC in activation of NF-κB signaling pathway. Lack of dietary OSC may activate the transcription factor NF-κB through the phosphorylation of IκB complex at the site of inflammation. NF-κB along with the subunits (p65 and p50) enters into the nucleus, thereby induces production of ROS, pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α) and enzymes (iNOS, COX-2), while their chronic production leads to increase risk of low-grade chronic inflammatory diseases.