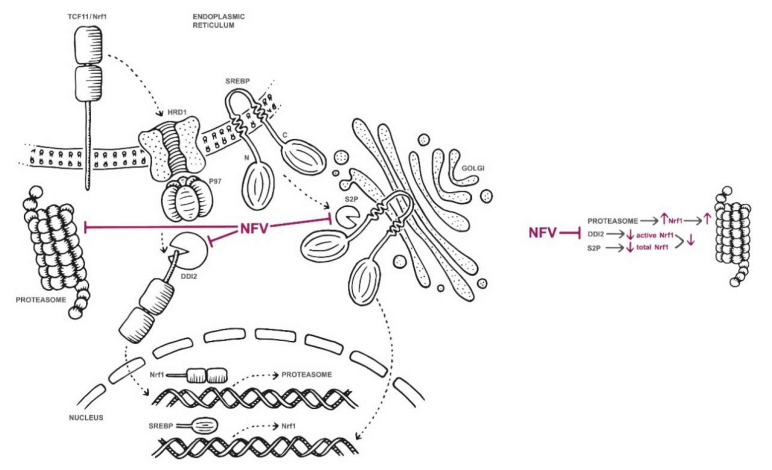
Figure 7.
Suggested model of nelfinavir’s modes of action related to proteasome synthesis and activity. At concentrations ≥40 μM, nelfinavir partially inhibits β1/β5 and β2 activity of the proteasome [24], thus activating TCF11/Nrf1-dependent proteasome re-synthesis (the bounce-back response). At the same time, nelfinavir inhibits UPR-activating protease S2P [19,20], which decreases active levels of the SREBP-1 transcription factor that is responsible for activating TCF11/Nrf1 transcription in the nucleus [38]. Therefore, TCF11/Nrf1 gene expression decreases. Furthermore, nelfinavir inhibits TCF11/Nrf1 proteolytic processing, resulting in lowered TCF11/Nrf1 protein levels in the nucleus. This decreases re-synthesis of proteasome genes. However, due to nelfinavir’s ability to activate ER and oxidative stress, proteasome re-synthesis might be, at least to some extent, re-driven by the Nrf2 pathway.