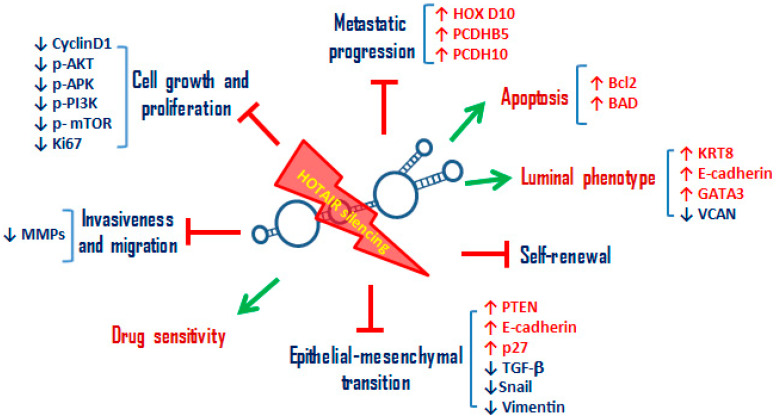
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the main cellular processes inhibited or activated by the silencing of HOTAIR in BC cells. HOTAIR knockdown in BC cells leads to the promotion of: (i) sensitivity to radiotherapy, chemotherapy, hormonal therapies and anti-HER2 therapies; (ii) luminal phenotype acquisition with the upregulation of luminal cytokeratins (KRT8), of cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin, and of transcription factor GATA3, responsible of luminal epithelial differentiation in the adult mammary gland. Furthermore, HOTAIR silencing in BC cells leads to the inhibition of: (i) cell growth and proliferation by downregulating the main signaling pathways involved in these cellular processes, such as PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK/ERK pathway, cyclin D1 and proliferation index Ki67; (ii) invasion and migration by downregulation of metalloproteinases; (iii) EMT by upregulating epithelial markers, such as E-cadherin, downregulating mesenchymal markers, such as Vimentin, and TGF-beta signaling; (iv) self-renewal, reducing colonosphere and mammosphere formation; (v) metastatic progression by upregulating metastasis suppressor genes, such as HOXD10, PCDHB5, and PCDH10. The green arrow indicates the activated processes, the symbol † the inhibited ones. KRT8: Keratin 8, GATA3: GATA Binding Protein 3, mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin, MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase, ERK: Extracellular regulated kinases, PCDHB5: Protocadherin Beta 5, PCDH10: Protocadherin 10.