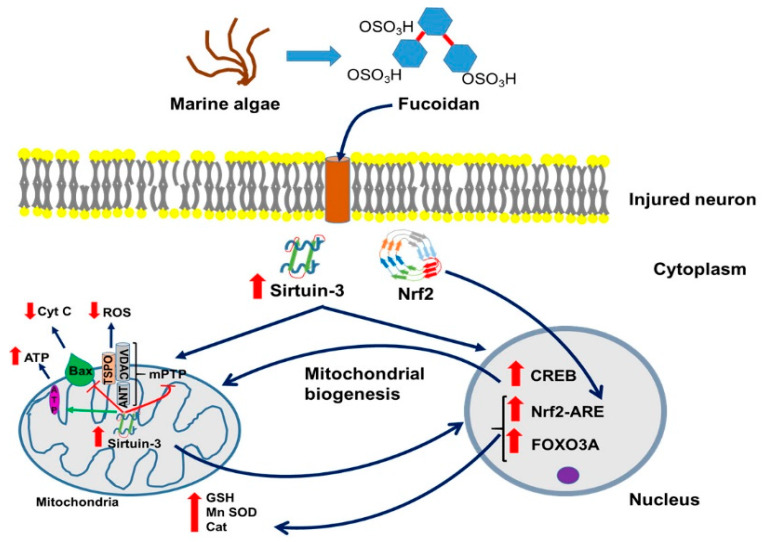
Figure 1.
Mechanism of action of fucoidan in traumatic brain injury (TBI). Fucoidan alleviates brain injury through upregulation of sirtuin, which decreases reactive oxygen species (ROS) overproduction by inhibiting the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening, and restores normal mitochondrial function via stimulation of ATP synthesis, and attenuates mitochondria-initiated apoptosis by decreasing leakage of cytochrome c from the mitochondria into the cytosol. Additionally, fucoidan stimulates expression of FOXO3A and Nrf-2-ARE genes, thus increasing glutathione (GSH) production and Mn-SOD and Cat activity.