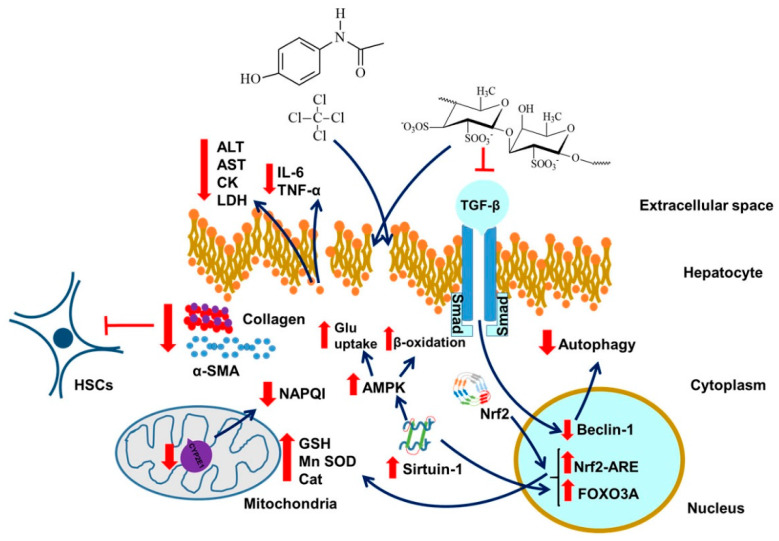
Figure 3.
Effects of fucoidan on liver injury. Damaging agents at the top left side, APAP and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), and protective fucoidan at the top right side. Fucoidan averts liver fibrosis by inhibiting HSCs production through optimal synthesis of collagen and alpha smooth muscle actin and prevents tissue damage by reducing transaminase release and restoring antioxidant potentials of cells. It decreases CYP2E1 activity, which reduces levels of toxic metabolites and inhibits TGF-β/Smad pathway, thereby hindering the occurrence of autophagosomes. Fucoidan also stimulates expression of sirtuin-1 in the liver, which activates AMPK and alleviates insulin resistance.