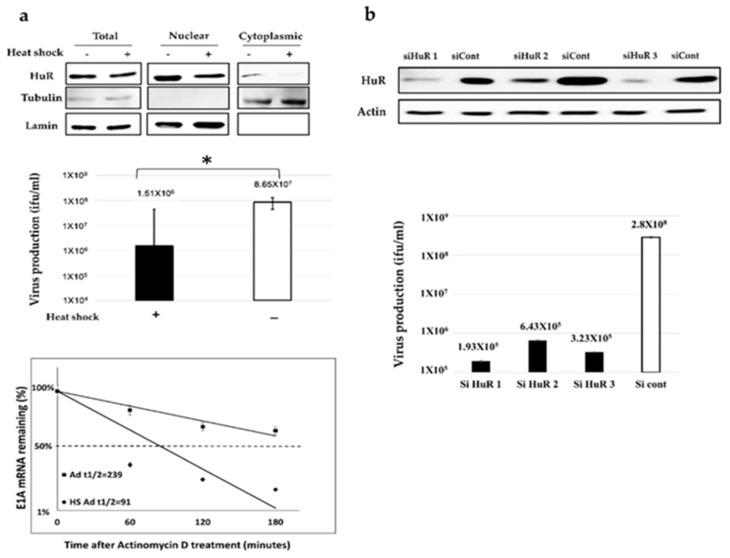
Figure 2.
The effects of HuR-depletion on E1A mRNA stabilization and Ad-fosARE replication. (a) HeLa cells were given heat-shock at 43 °C for 2 h, and the amount of HuR in total, nuclear, and cytoplasmic fraction were determined using western blot analysis. β-tubulin and lamin expression were used as cytoplasmic and nuclear fraction markers (top). Virus production was assessed, and the values were compared to the non-treated cells (middle) (* indicates p < 0.05). HeLa cells were infected with Ad-fosARE (MOI 10 ifu/cell) and heat-shocked immediately after infection at 43 °C for 2 h. Transcriptions were inhibited by actinomycin D 5 µl/mL for 60, 120, and 180 minutes. After the indicated periods, cells were harvested and extracted for total cellular RNA. mRNA levels are quantified by quantitative real-time RT-PCR experiments, using Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) as a normalization control. Graphs depict the percentage of remaining E1A mRNA levels with GAPDH mRNA and compared with the standards of normalized mRNA species measured immediately after the addition of actinomycin D and which were set as 100%. The half-lives of the mRNAs (min) are indicated as t½ (bottom). (b) HeLa cells were transfected with a HuR targeting siRNA (HuR 1, HuR 2, and HuR 3) and a negative control siRNA, and the expression of HuR was estimated by western blot analysis. (top) HuR KD-HeLa cells were infected with Ad-fosARE, and viral titers were determined as described in materials and methods after 48 h of virus infection. (bottom) siHuR, siRNA targeting HuR; siCont, control siRNA treated cells. Data shown above presented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments.