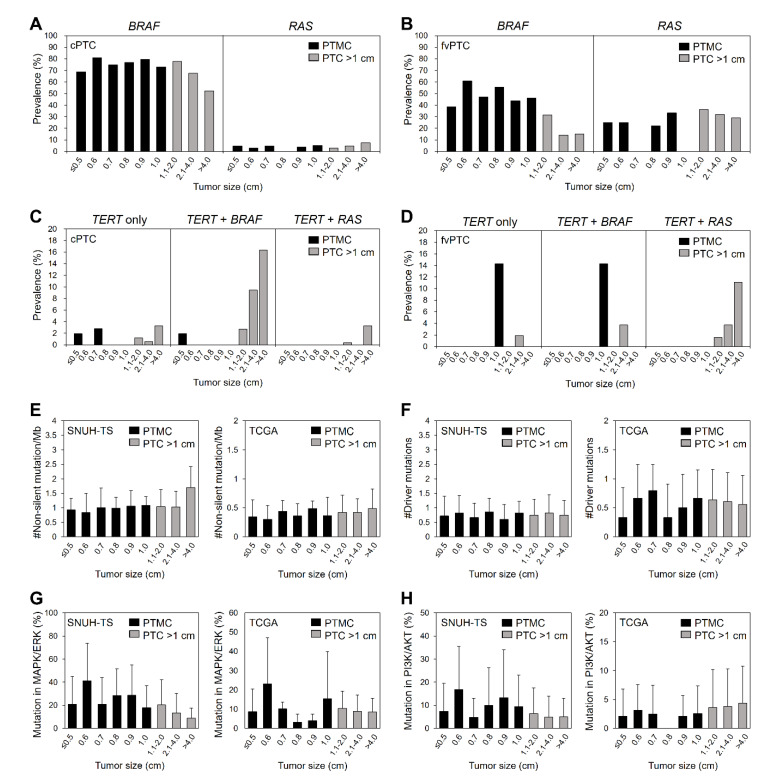
Figure 1.
Genomic characteristics of papillary thyroid carcinoma according to tumor size. Prevalence of BRAFV600E and RAS mutations according to tumor size in (A) classical (n = 2954 and 851 for BRAFV600E and RAS, respectively) and (B) follicular variant (n = 342 and 217 for BRAFV600E and RAS, respectively) PTCs. Prevalence of TERT promoter mutations (TERT alone, TERT + BRAF, and TERT + RAS) according to tumor size in (C) classical (n = 707) and (D) follicular variant (n = 184) PTCs. (E) Tumor mutational burden, (F) number of driver mutations, and (G) proportions of non-silent mutations involved in mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway and (H) in phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) pathways compared to total non-silent mutations, according to tumor size of PTC in the SNUH targeted sequencing (SNUH-TS, n = 221) and TCGA (n = 496) datasets. cPTC, classical papillary thyroid carcinoma; fvPTC, follicular-variant papillary thyroid carcinoma; PTMC, papillary thyroid microcarcinoma; PTC, papillary thyroid carcinoma.