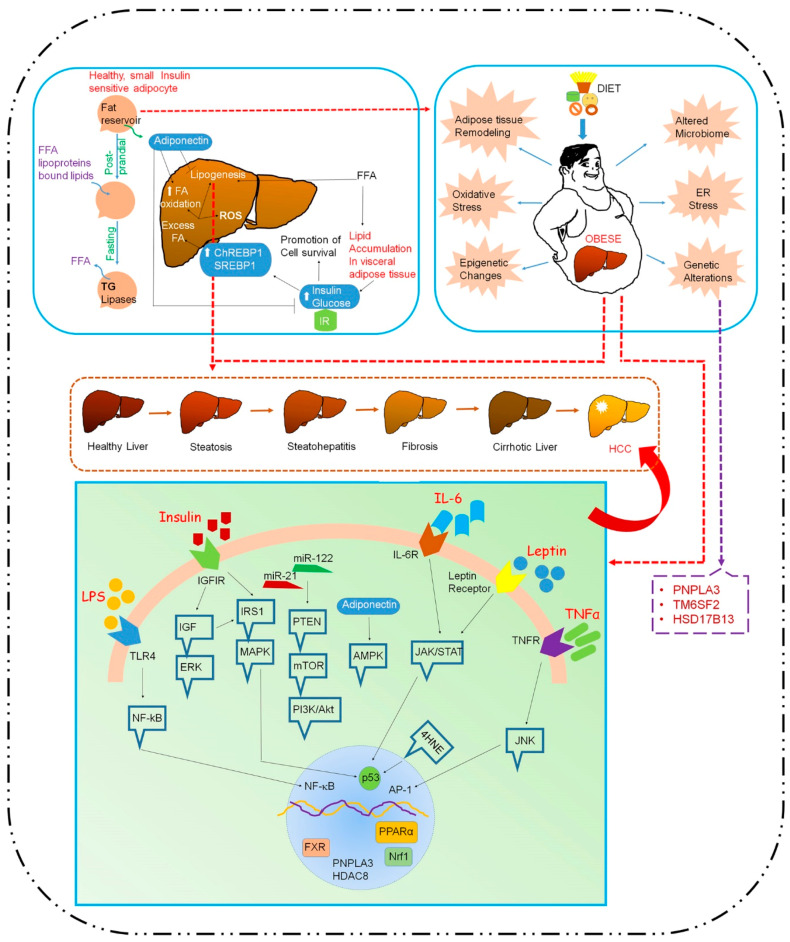
Figure 1.
Molecular signaling pathways promoting HCC in the presence of obesity. Over-nutrition and a sedentary lifestyle induce adipose tissue remodeling, microbiome alteration, and ER and oxidative stress. These modifications, in association with genetic factors such as PNPLA3 and epigenetic changes, lead to the dysregulation of adipokine secretion and activation of the PI3K/Akt, JAK/STAT, NF-κB, mTOR, 4-HNE, and NRF-1 oncogenic pathways. Healthy adipocytes, in response to the above stimuli, absorb lipids and secrete adiponectin, which promotes insulin sensitivity and FA oxidation and suppresses lipogenesis. In the fasting state, adipocytes release FAs whereas in obesity, they swell and dedifferentiate, releasing less adiponectin. Subsequent macrophage infiltration contributes to inflammation. Lipolysis releases free fatty acids (FFAs), leading to triglyceride accumulation in VAT that generates IR. High FFAs and IR lead to steatosis, followed by hepatic lipogenesis by the transcriptional regulators SREBP1 and ChREBP1. Steatosis is mostly benign, but in the presence of excess FAs that are not converted into triglyceride, there is an overload of mitochondrial FA oxidation with the generation of ROS that promotes liver tissue damage and inflammation (NASH). IR facilitates high circulating glucose and insulin, which promotes cell survival and a tumor microenvironment. The persistent conditions promote DNA damage and HCC development. Additionally, obese adipose tissues promote an inflammatory response that contributes to liver damage, an impaired immune response and HCC progression. trans-4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE); adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK); endoplasmic reticulum (ER); insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1); interleukin-6 (IL-6); insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1); mammalian target of rapamycin complex (mTOR); nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB); nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 1 (Nrf-1); phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K); PI3K/phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN); toll-like receptor (TLR); tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα); peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α); fatty acid (FA); visceral adipose tissue (VAT); insulin resistance (IR); sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP1); carbohydrate regulatory-binding protein (ChREBP1); reactive oxygen species (ROS); nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).