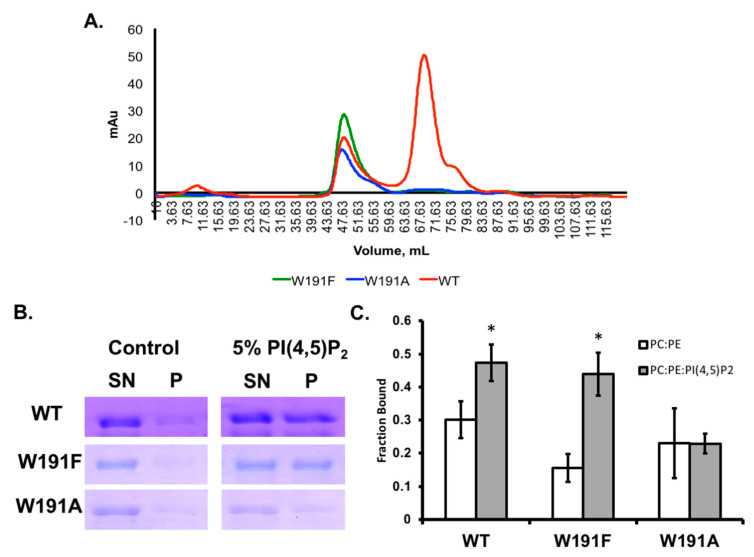
Figure 4.
WT VP40 and Trp191 mutant dimer and octamer propensity and lipid binding analysis. (A) Size exclusion chromatography was performed post-affinity chromatography for WT VP40 (red), W191A (green), or W191F (blue). WT exhibited the characteristic dimer peak between 67 and 71 mL as well as an octamer peak at 47–51 mL. In contrast, W191A and W191F were predominantly octamers and dimer populations were barely detectable. The size exclusion column was routinely calibrated with high molecular weight standards from Cytiva (43,000–669,000 Da) (Marlborough, MA, USA). (B) A vesicle binding assay was performed as previously described [14] for WT, W191A, and W191F using control and PI(4,5)P2 containing vesicles where the bound (P—pellet) and unbound (SN—supernatant) fraction were separated by centrifugation. (C) Quantification of three independent experiments for the fraction of VP40 or mutant bound to control or PI(4,5)P2 containing vesicles. * p < 0.05.