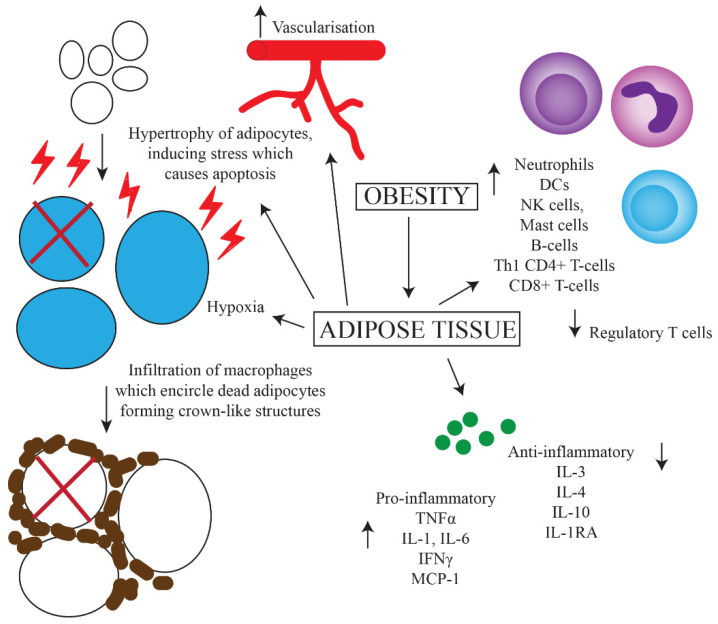
Figure 1.
Predominant mechanisms of chronic inflammation caused by obesity. Increased uptake of nutrients leads to greater storage of fats and hence hypertrophy of adipocytes. This results in increased intracellular stress and upregulation of apoptotic genes, leading to apoptosis. Increased vascularization, hypoxia, cell death and upregulation of MHC-II on adipocytes leads to the influx of various inflammatory cells including macrophages, which surround dead adipocytes forming crown-like structures. There is also increased secretion of pro-inflammatory, and decreased secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines.