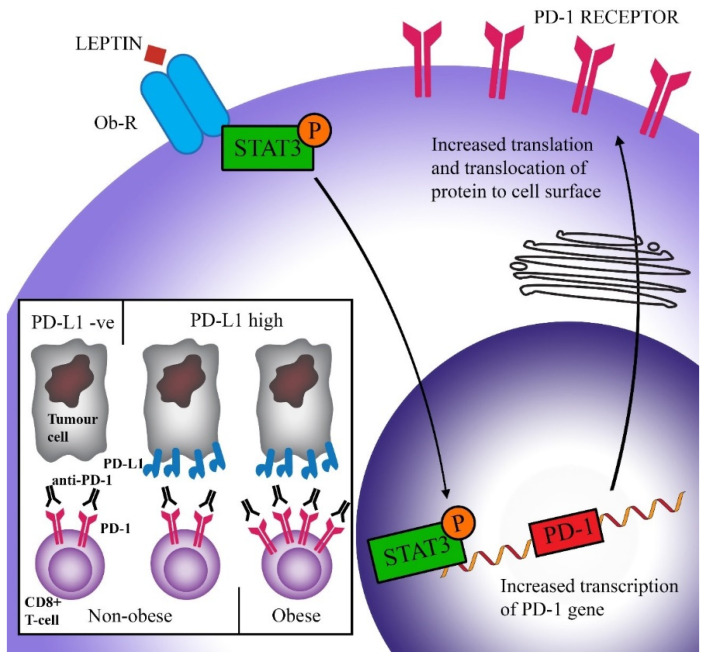
Figure 2.
Scheme of a proposed pathway causing increased efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade in obese patients. Leptin binds to its receptor (Ob-R) on CD8+ T-cells and causes the activation (via phosphorylation) of the transcription factor STAT3. STAT3 triggers the transcription of the PD-1 gene and subsequent expression of the PD-1 protein on the cell surface. Higher PD-1 levels are correlated with increased exhaustion (activation by PD-L1 reduces T-cell proliferation, survival, and production of cytokines). However, increased PD-1 expression facilitates greater success of anti-PD-1 therapy, leading to increased overall survival in obese patients.