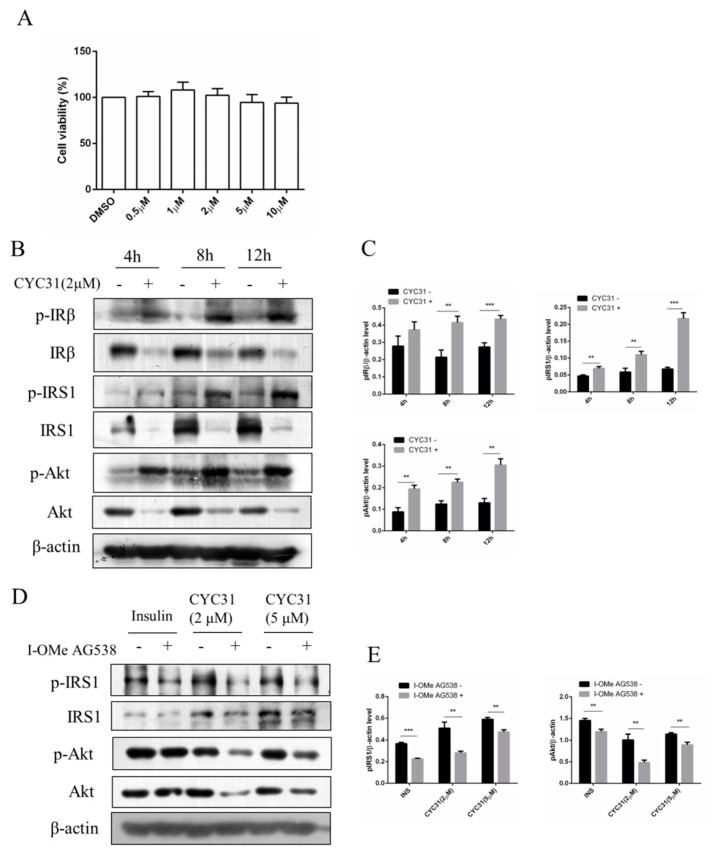
Figure 2.
Increased insulin signaling by CYC31: (A) The cytotoxicity of CYC31 in C2C12 skeletal cells. C2C12 myotubes were treated with different dosages of CYC31 for 24 h, and the cell viability was measured by MTT assay (B) Time-dependent activation of insulin signaling by CYC31: Serum-starved C2C12 myotubes were treated with 2 µM CYC31 for 4–12 h. The phosphorylation of IRS1, IRβ, and Akt, and corresponding total proteins were detected by immunoblotting (C) Relative phosphorylation levels of IRS1, IRβ, and Akt. Band density was measured by Image J software and normalized to β-Actin. (D) Effect of I-OMe AG538 (IR kinase inhibitor) on CYC31-treated C2C12 skeletal cells. Serum-starved C2C12 myotubes were pretreated with/without 50 µM I-OMe AG538 for 3 h and then exposed to CYC31 for another 8 h. Then, the phosphorylation of IRS1, IRβ, and Akt were detected by western blotting. (E) Relative phosphorylation levels of IRS1 and Akt. Band density was measured by Image J software and normalized to β-Actin. Data was shown as mean ± SD values (n = 3), ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.