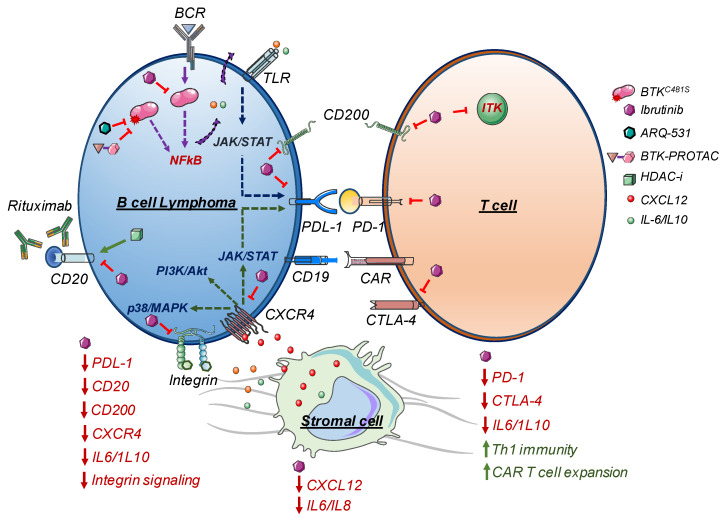
Figure 1.
Ibrutinib’s mechanism of action and strategies to overcome ibrutinib resistance. Ibrutinib treatment has been shown to negatively influence TME and have immunomodulatory functions. Ibrutinib inhibits JAK/STAT signaling through CXCR4/CXCL12, thereby preventing expression of immunosuppression of PD-L1/CD200 on tumor cells and PD1/CTLA4 on T-cells. Additionally, ibrutinib has shown to promote Th1-type immunity and, therefore, significantly improved CAR T-cell expansion upon ibrutinib treatment. Ibrutinib is unable to target BTK mutants; therefore, third-generation BTK inhibitors or BTK-PROTAC can prevent BTK-mutant-dependent ibrutinib resistance development.