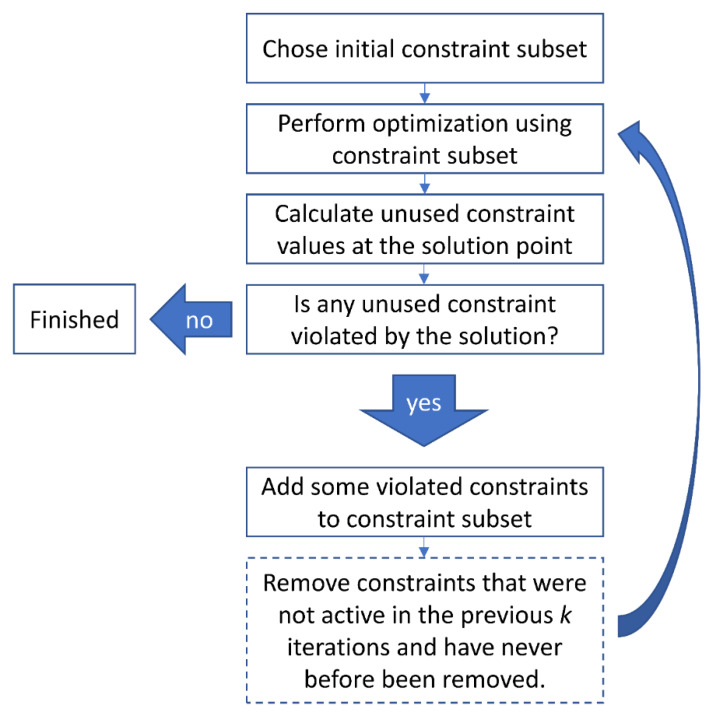
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the iterative solution algorithm. The algorithm initially selects a small subset of all healthy (=constraint) voxels to be considered during the targeted heating calculation. After performing the optimization, the resultant specific absorption rate (SAR) in the unconsidered voxels is calculated to find regions where the found solution violates the constraints (i.e., leads to undesired heating in healthy regions). A small number of the healthy voxels experiencing the strongest heating are added to the constraint subset and the optimization is repeated. This process is iterated until no further constraints are violated by the solution. The last step in the dashed outline is optional and only required if the number of constraints has increased to a level that significantly impacts each iterative solution runtime.