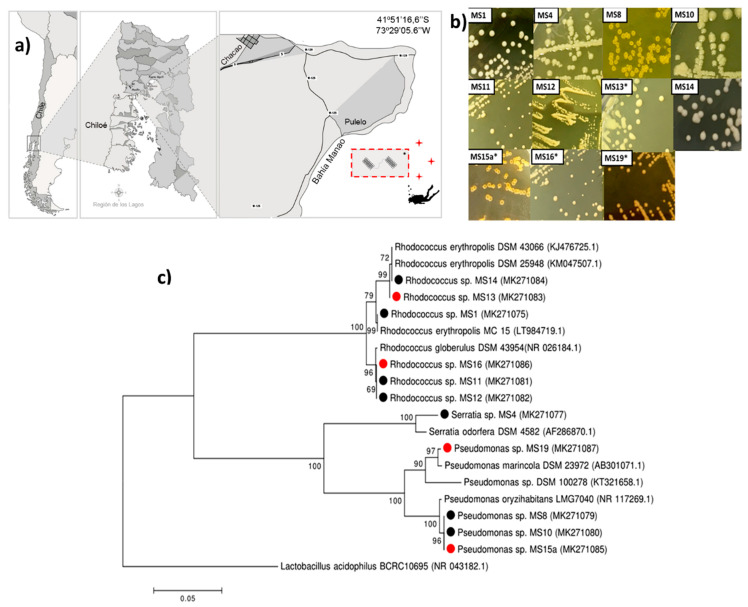
Figure 1.
Map of sampling site, geographical position, colony morphologies, phylogeny, and biodiversity of cypermethrin-degrading and biosurfactant-producing bacterial strains isolated from the Chilean Northern Patagonia samples. (a) Map of the sampling sites in the Manao Bay: samples were collected from marine sediments at 25 m depth. The asterisk indicates salmon farming center. Crosses mark the three sampling sites. (b) Colony morphology, in TSA medium, of cypermethrin-degrading and biosurfactant-producing bacterial strains isolated by enrichment using cypermethrin as the sole carbon and energy source. (c) Phylogenetic tree of cypermethrin-degrading and biosurfactant-producing bacterial strains isolated from the Northern Patagonia; black circles indicate cypermethrin-degrading and biosurfactant-producing isolated bacterial strains. Red circles indicate strains selected for genomic analysis.