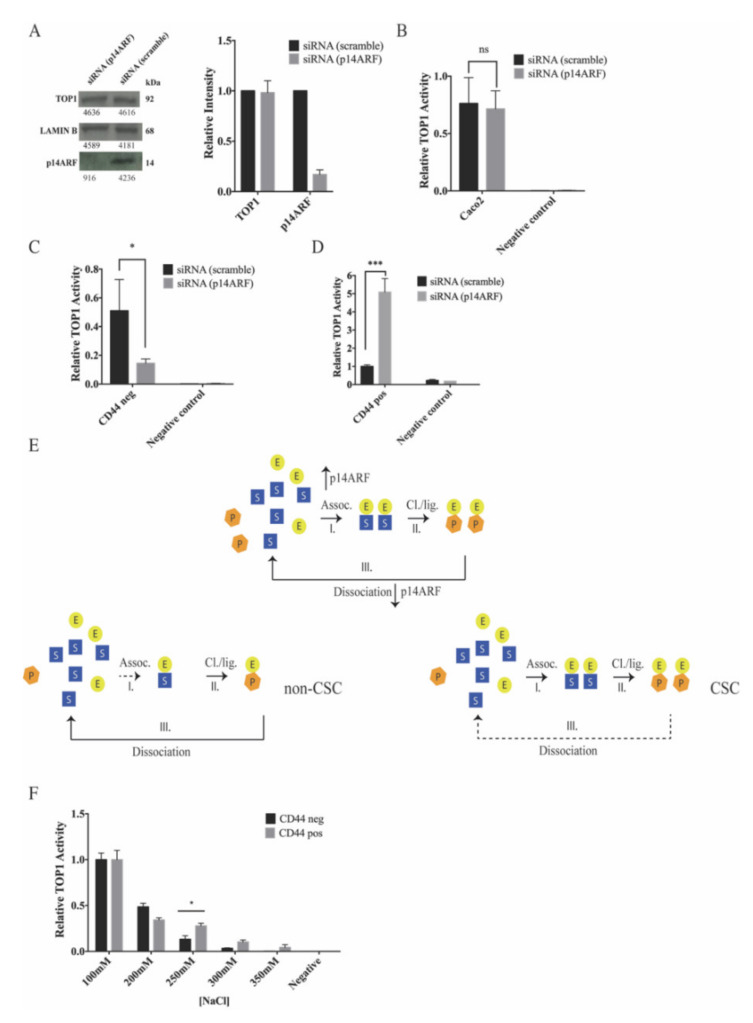
Figure 4.
Effect of p14ARF downregulation on topoisomerase 1 activity. (A) Left panel, Western blot analysis of whole cell extracts from unsorted Caco2 cells transfected with scrambled siRNA (siRNA (scramble)) or p14ARF specific siRNA (siRNA (p14ARF)) developed by using anti-TOP1, anti-p14ARF, or anti-LAMIN B antibodies. Right panel, graphical depiction showing the results of the densitometrically quantified bands shown in the Western blot. The intensity of the p14ARF or TOP1 specific bands was normalized relative to the intensity of the LAMIN B bands. Data were plotted as mean +/− standard error of the mean (SEM). (B) Measurement of TOP1 activity by rolling-circle enhanced enzyme activity detection (REEAD) in whole cell extracts from Caco2 cells transfected with siRNA (scramble) (black bars) or siRNA (p14ARF) (grey bars). The REEAD signals detected on an average of 12 microscopic images were counted using the ImageJ software and the result was normalized against the number of signals obtained by analyzing the activity of purified TOP1. The signals were normalized as reported by Stougaard et al. [50]. All data were plotted as mean +/− SEM, ns = not significative, Welch’s test, n = 6. (C) Same as (B), except that non-CSC-like cells (CD44 negative) were analyzed. The non-CSC-like cells were obtained by treating the cells with NaBt, giving approx. 100% CD44 negative cells. The data were plotted as mean +/− SEM. * p = 0.03, Welch’s test, n = 6. (D) Measurement of TOP1 activity in the whole cell extracts from Caco2 CSC-like (CD44 positive) cells transfected with siRNA (scramble) (black bars) or siRNA (p14ARF) (grey bars). The CSC-like (CD44 positive) cells were captured onto a glass slide by using anti-CD44 antibody and the TOP1 activity measured by using the On-Slide-REEAD as described by Keller et al. [51]. The REEAD signals were counted using the ImageJ software and the result was normalized against the number of signals obtained by analyzing the activity of purified TOP1. The signals were normalized as reported by Andersen et al. [52]. The data were plotted as mean +/− SEM. *** p = 0.0002, Welch’s test, n = 6. (E) Schematic illustration of the catalytic steps that determine the reaction rate of TOP1. First, the enzyme (yellow circle, E) associates (I) with the substrate (blue square, S) to form a non-covalent binding complex. Thereafter, the enzyme performs cleavage–ligation (II) to generate a product (orange hexagon, P) still associated with the enzyme. Finally, the enzyme dissociates (III) from the product and is ready to perform another round of catalysis. p14ARF stimulates non-covalent DNA binding. Thereby it stimulates association and inhibits dissociation (illustrated by arrows pointing up for stimulation and down for inhibition). The lower left panel illustrates how a weakened association in non-CSC cells will affect activity while the lower right panel illustrates how a weakened dissociation in CSC cells will affect activity. (F) Measurement of TOP1 activity in the nuclear extracts from Caco2 non-CSC-like (CD44 negative) (black bars) and Caco2 CSC-like (CD44 positive) (grey bars) FACS sorted cell subpopulations, respectively. The activity was measured by REEAD at different NaCl concentrations as reported on the x-axis. The REEAD signals were counted using the ImageJ software and the result was normalized against the number of signals obtained by analyzing the activity of purified TOP1. All data were plotted as mean +/− SEM. * p < 0.04, Welch’s t-test. The whole western blot figures please find in Figure S10B.