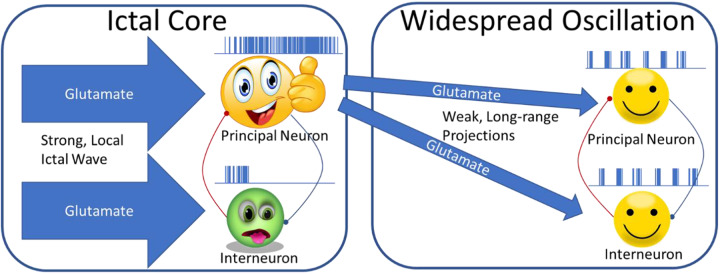
Figure 1.
Neurons in the ictal core receive strong glutamatergic input from the locally propagating seizure. This drives interneurons into depolarization block, while principal neurons fire at a high rate. Excitatory neurons in the ictal core provide synchronous weak drive to distant principal cells and interneurons. Feedback inhibition in these distal networks generates an oscillation that is synchronized with spiking in the ictal core.