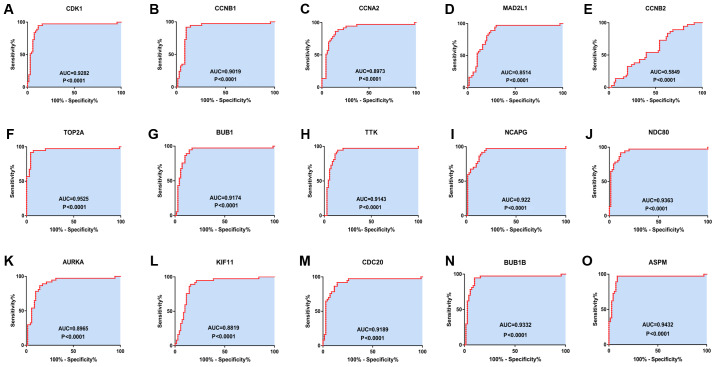
Figure 5.
Receiver operating characteristics curves for the 15 hub genes to identify HCC tissue from normal tissue. (A) CDK1 (AUC=0.9282, P<0.0001), (B) CCNB1 (AUC=0.0.9019, P<0.0001), (C) CCNA2 (AUC=0.8973, P<0.0001), (D) MAD2L1 (AUC=0.8514, P<0.0001), (E) CCNB2 (AUC=0.5849, P=0.1496), (F) TOP2A (AUC=0.9525, P<0.0001), (G) BUB1 (AUC=0.9174, P<0.0001), (H) TTK (AUC=0.9143, P<0.0001), (I) NCAPG (AUC=0.922, P<0.0001), (J) NDC80 (AUC=0.9363, P<0.0001), (K) AURKA (AUC=0.8965, P<0.0001), (L) KIF11 (AUC=0.8819, P<0.0001), (M) CDC20 (AUC=0.9189, P<0.0001), (N) BUB1B (AUC=0.9332, P<0.0001) and (O) ASPM (AUC=0.9432, P<0.0001). CDK1, cyclin-dependent kinase 1; CCNA2, cyclin A2; MAD2L1, mitotic arrest deficient 2 like 1; TOP2A, DNA topoisomerase IIα; BUB1, budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1; TTK, TTK protein kinase; NCAPG, non-SMC condensin I complex subunit G; NDC80, NDC80 kinetochore complex component; AURKA, aurora kinase A; KIF11, kinesin family member 11; CDC20, cell division cycle 20; ASPM, abnormal spindle microtubule assembly; AUC, area under the curve.