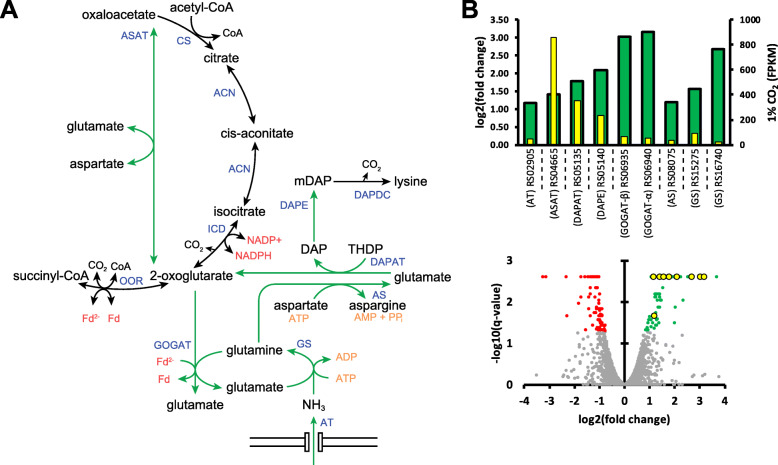
Fig. 6.
a Overview of the statistically significantly overexpressed reaction (green) involved in glutamate metabolism during CO2 limitation. ACN, aconitase; AS, aspargine synthase (CDQ83_RS08075); ASAT, aspartate transaminase (CDQ83_RS04665); AT, ammonium transporter (CDQ83_RS02905); CS, citrate synthase; DAPAT, l,l-diaminopimelate aminotransferase (CDQ83_RS05135); DAPDC, diaminopimelate decarboxylase; DAPE, diaminopimelate epimerase (CDQ83_RS05140); GOGAT, ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase (CDQ83_RS06935–40); GS, glutamine synthethase (CDQ83_RS15275 & CDQ83_RS16740); ICD, isocitrate dehydrogenase; OOR, 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase. b Results from differential expression analysis for the genes involved in the highlighted reactions in A. Positive fold change represents an increase of mRNA coverage during CO2 limitation (i.e. 1% versus 20% CO2). In the volcano plots, green data points depict genes with a statistically significant increase (i.e. q-value < 0.05) during CO2 limitation and red data points those with a statistically significant decrease in coverage during CO2 limitation. Yellow data points correspond to the genes presented in the accompanying bar graph. In the bar graphs, the wide bars display the log2(fold change) and the narrow (yellow) bars display the mean coverage in FPKM during 1% CO2