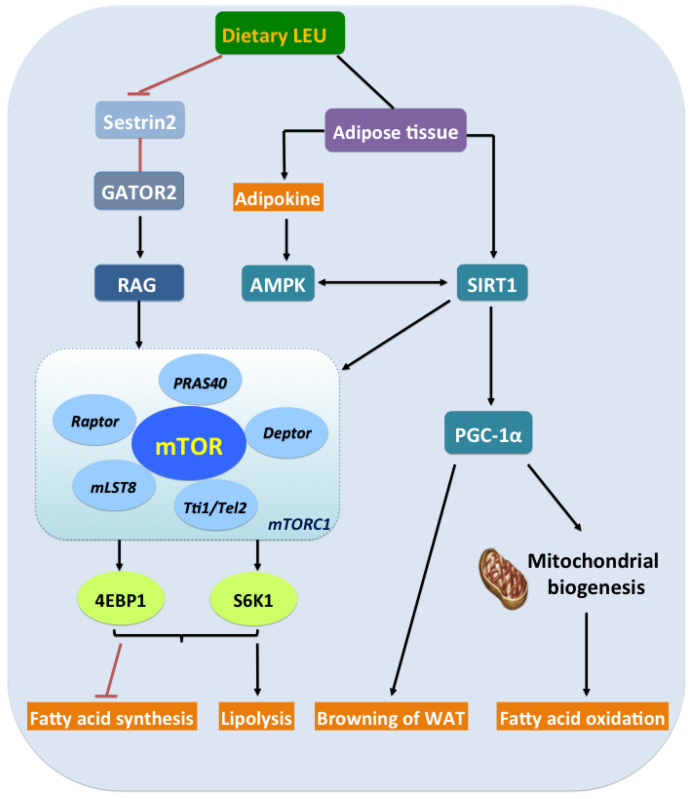
Figure 2.
Dietary leucine effects on lipid metabolism in adipose tissues. After ingestion, leucine binds to Sestrin2, and then activates mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), facilitates lipolysis, and inhibits fatty acid synthesis by modulating the substrates such as translational inhibitor 4E-binding protein-1 (4EBP1) and S6 kinase 1 (S6K1). It also regulates adipokine synthesis/secretion and adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK)–silent information regulator of transcription 1 (SIRT1)–proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) energy axis in adipose tissue, thus modulating mitochondrial biogenesis, promoting browning and fatty acid oxidation.