Fig. 4A-G.
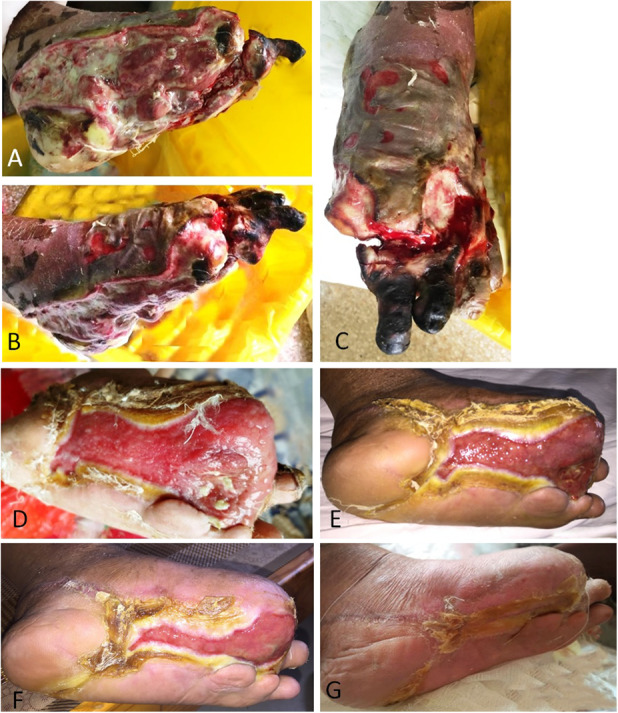
This figure shows the effects of tibial cortex transverse distraction in a 67-year-old man with severe and resistant plantar diabetic foot ulcer. (A-C) These images show ulcers before surgery. Almost all planta were involved, and purulent secretion, cacosmia, and swelling were obvious. The foot muscles, bone, and tendon were exposed. The first toe had been amputated and gangrene of the second and third toes was evident. Foot swelling was apparent. After débridement, the second and third toes were removed. (D) Four weeks postoperatively, the wound was much smaller, with epithelization at the edges, without pain or infection and with minimal swelling. The wound bed was clean and covered by robust granulation tissue. (E-F) These images show the foot at 8 weeks and 10 weeks postoperatively, respectively. (G) The ulcer was completely healed at 12 weeks postoperatively.
