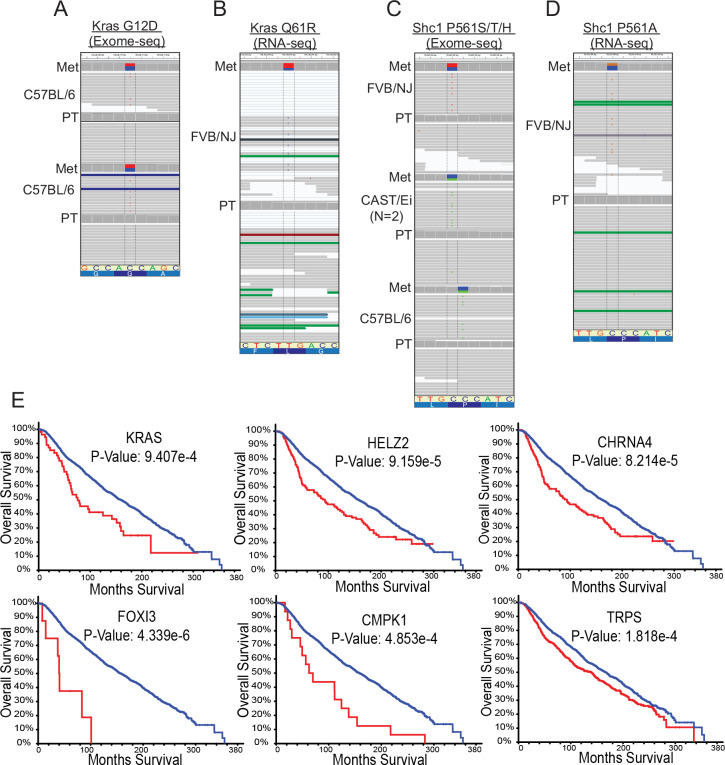
Fig 3. Metastasis-specific mutations are recurrent and stratify patient outcome.
IGV screen shots showing allele frequency in the blue and red boxes, representative SNV reads, mutated codon letter, tissue type, and mouse strain. A, Exome-seq identified a C (blue) to T (red) SNV within Kras resulting in the G12D amino acid substitution in metastases from two C57BL/6J x PyMT animals. B. RNA-seq identified a T (red) to C (blue) SNV within Kras resulting in the Q61R amino acid substitution in a metastatic lesion from one FVB/NJ x PyMT animal. C, Exome-seq identified C (blue) to T (red) and C (blue) to A (green) SNVs in metastases from three animals (FVB/NJ, CAST/Ei (2 mets from 1 mouse with same SNV), and C57BL/6J x PyMT) resulting in the P561S/T or H amino acid substitutions, respectively. D, RNA-seq identified a C (blue) to G (orange) SNV resulting in the P561A amino acid substitution in one FVB/NJ x PyMT animal. E. Kaplan-Meier plots generated using METABRIC for the top six genes identified with metastasis-driver SNVs by exome-seq in mice that most significantly stratify patient survival when altered in primary tumor tissue (blue = no CNV, red = CNV present). PT, primary tumor; Met, metastasis.