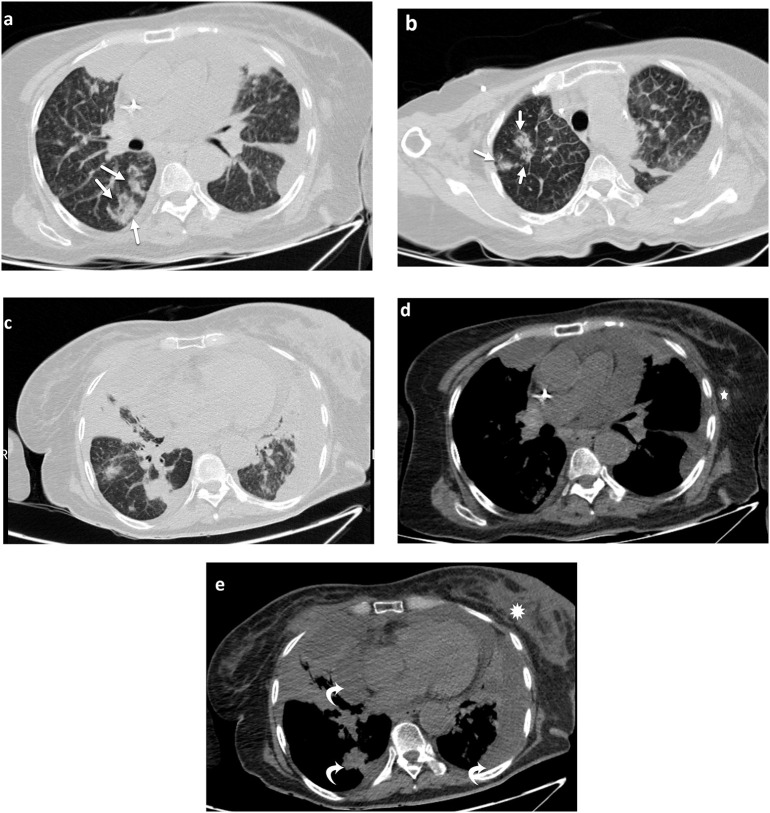
Fig. 7.
COVID-19 infection in breast cancer. A fifty-year-old female with history of metastatic left breast cancer was referred for CT chest due to new-onset fever. Axial CT (a), (b), and (c) demonstrate scattered bilateral GGOs and consolidations (thick arrows) concerning for superimposed COVID-19 infection on pulmonary metastases. Also, there is pleural fluid in the left major fissure and interlobular septal thickening (a, b). Moreover, left axillary lymphadenopathy (d; ☆) the primary breast cancer (e; *), and parenchymal, pleural and pericardial metastases and effusion (e; curved arrows) are identified.