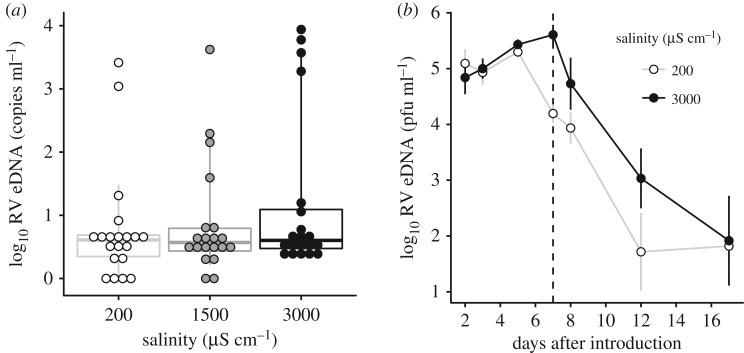
Figure 4.
Effects of road salt on the shedding rate and persistence of ranavirus from infected larvae from two laboratory experiments. (a) The concentration of ranavirus DNA shed into housing water (eDNA) in points and box plots showing median, lower and upper quantiles of shed DNA, whiskers extend to 10th and 90th quantiles, representing the increase in ‘super-shedders’ in the salinity treatments (n = 20). (b) Average (±s.e.m., n = 4 aquaria) log10 ranavirus eDNA concentration in aquaria water after six ranavirus-infected wood frog larvae were introduced. Larvae were removed at 7 d (vertical dotted line), and eDNA sampling continued to examine decay rates.