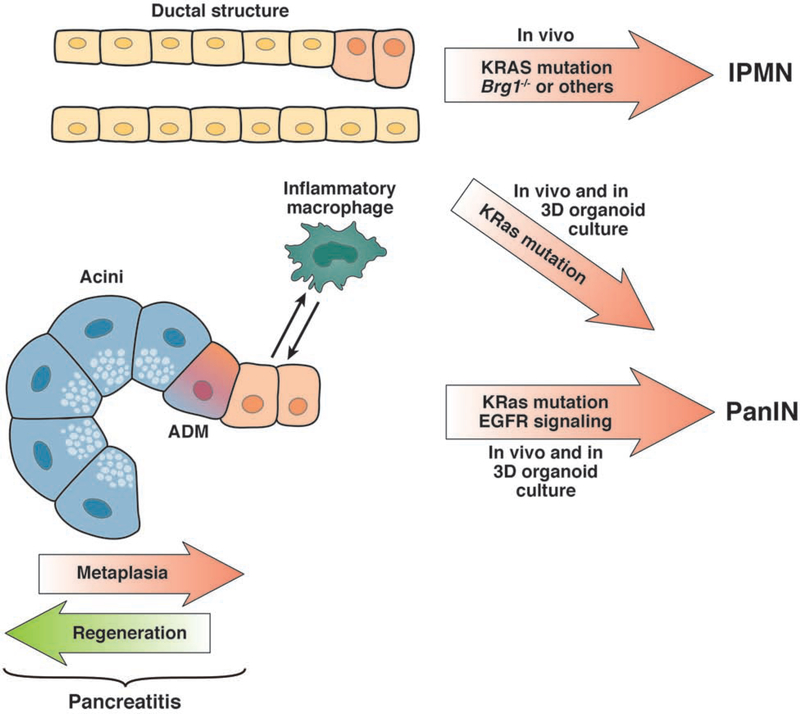
Figure 1. Cells of origin for PDA.
There is evidence that PDAs develop from acinar and/or duct cells. In 3-dimensional organoid culture, duct cells that express oncogenic KRAS can develop into PanIN-like cells; when these are transplanted into mice they form low-grade dysplasias. After additional disruption of Brg1, duct cells with a KRAS mutation can progress to IPMN. Acinar cells are highly plastic and, in crosstalk with inflammatory macrophages, can transdifferentiate to a ductal phenotype (acinar to ductal metaplasia). With an oncogenic KRAS mutation these ADM cells stay locked in a ductal stage, show increased EGFR signaling, and progress to PanIN and PDA.