Figure 2.
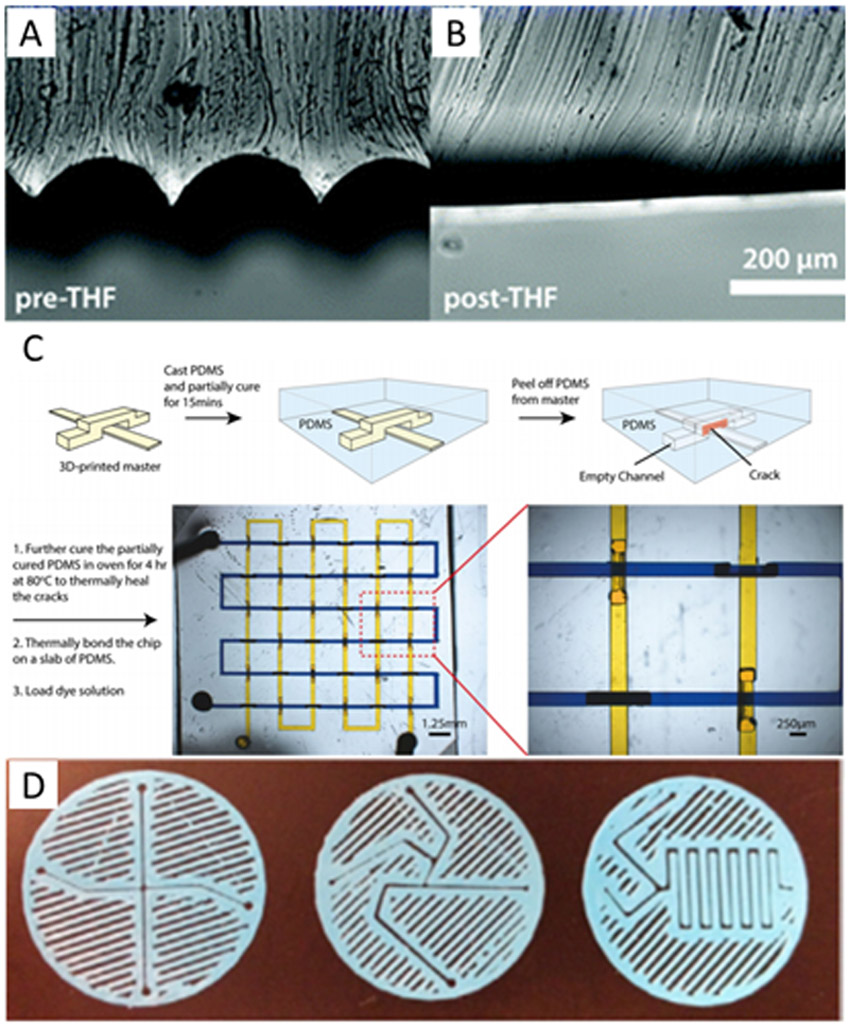
Template and surface 3D printed microfluidic devices. A-B) Images showing the surface roughness of a polylactic acid FDM template before and after smoothing with tetrahydrofuran solvent. Republished with permission of the Royal Society of Chemistry, from ref. 69; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center. C) A method of casting a fully three-dimensional device. PDMS is cast over a 3D printed template and allowed to partially cure. The PDMS is cracked and peeled off the template then allowed to fully cure before filling with fluid for experiments. Reprinted by permission from ref. 75, copyright 2015 Springer Nature. D) Sandwich-style planar mixers printed using FDM then sandwiched between two surfaces with interface connections to form fluidic devices. Republished from ref. 82 with permission of IOP Publishing; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center.
